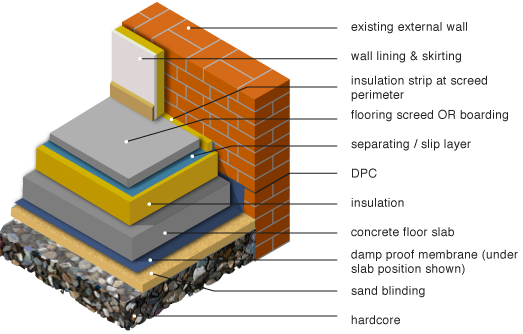
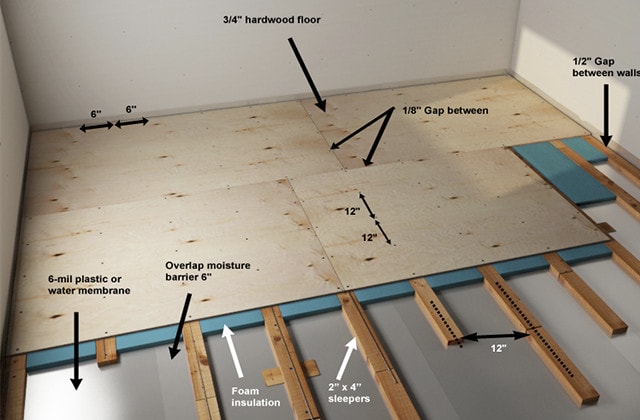
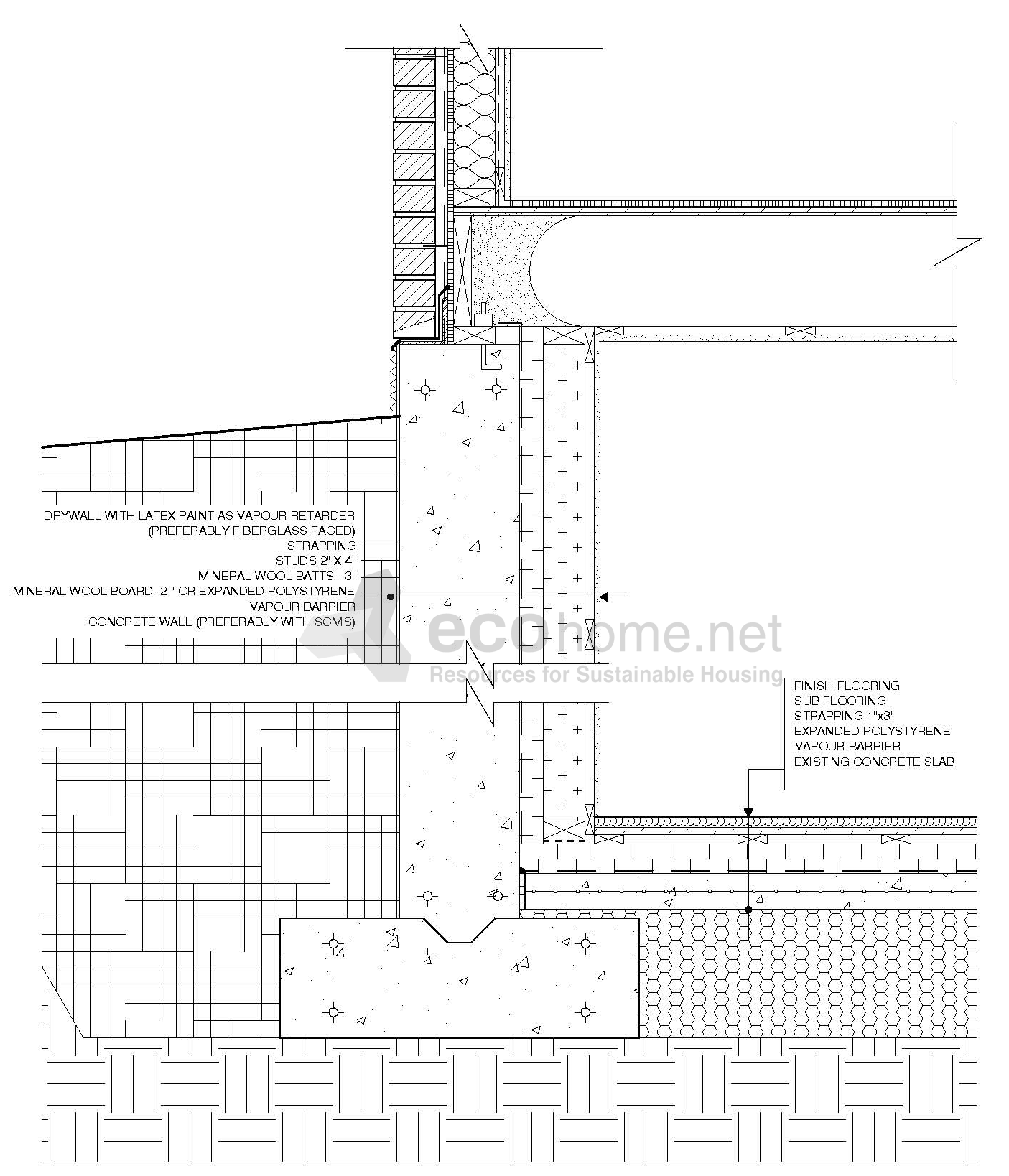
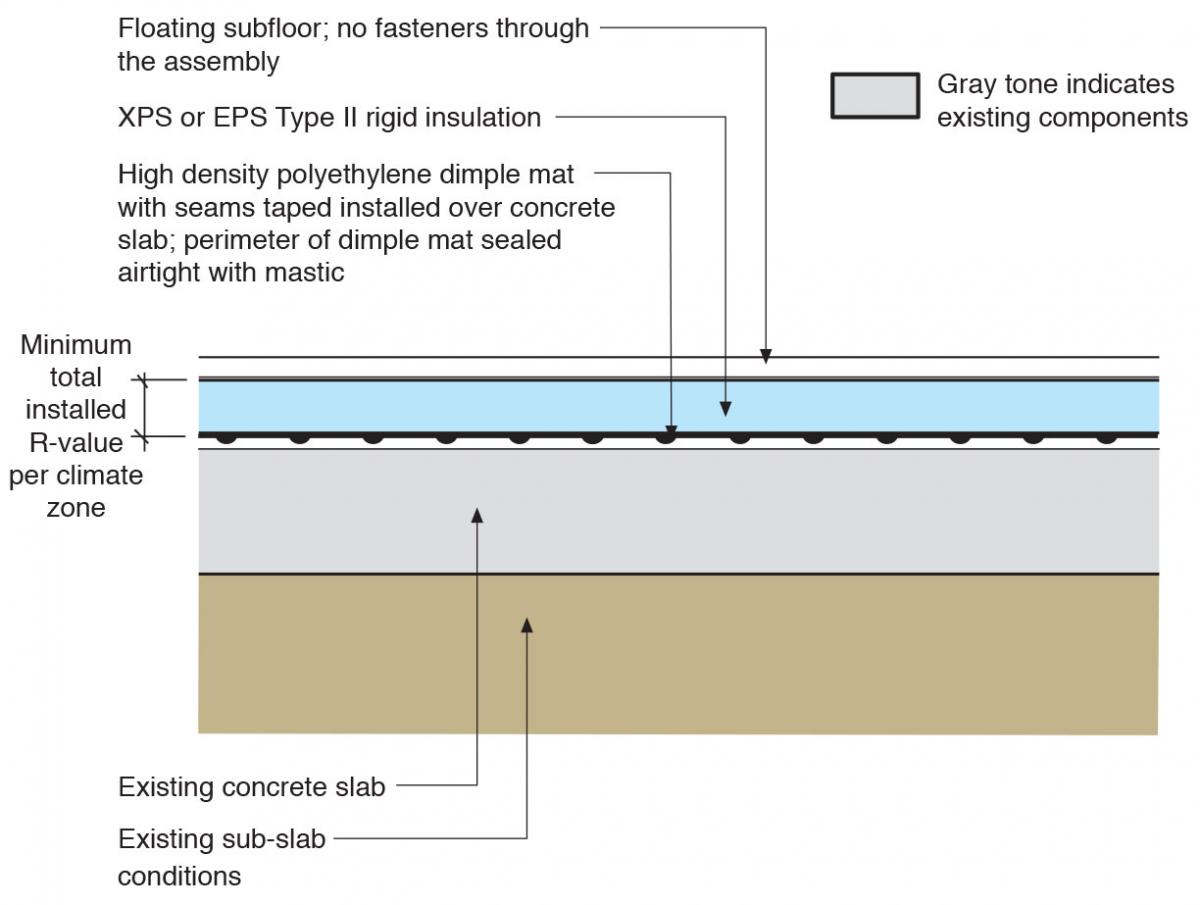
The Importance of Basement Floor Insulation
Basement floor insulation is a critical component of any home’s energy efficiency and comfort. Often overlooked, insulating your basement floor can have a significant impact on maintaining a consistent temperature throughout your home, reducing energy bills, and preventing moisture-related issues. Here’s why basement floor insulation matters:
- Moisture Control: Basements are prone to moisture buildup, which can lead to mold, mildew, and musty odors. Insulating the basement floor helps create a barrier against moisture infiltration from the ground, keeping the space dry and healthy.
- Energy Efficiency: Uninsulated basement floors can act as a significant source of heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. By insulating the basement floor, you can minimize thermal bridging and reduce the workload on your HVAC system, leading to lower energy consumption and utility costs.
- Enhanced Comfort: Insulating the basement floor not only helps regulate indoor temperatures but also makes the space more comfortable year-round. A properly insulated basement feels warmer in winter and cooler in summer, creating a more pleasant living environment for you and your family.
- Protection Against Cold Floors: Cold basement floors can make the entire space feel chilly and uncomfortable, especially during the winter months. Insulation provides a thermal barrier that helps prevent heat loss through the floor, keeping it warmer and more comfortable underfoot.
- Prevention of Structural Damage: In regions with freeze-thaw cycles, uninsulated basement floors are susceptible to frost heave, which can cause cracks and damage to the foundation. Insulation helps stabilize the temperature of the basement floor, reducing the risk of structural issues over time.
- Noise Reduction: Insulating the basement floor can also help dampen sound transmission from foot traffic, appliances, and other sources, creating a quieter and more peaceful living environment throughout the house.

Traditional vs. Modern Basement Floor Insulation Techniques
When it comes to insulating basement floors, homeowners have a choice between traditional and modern techniques. Each approach comes with its own set of advantages and considerations. Here’s a comparison of traditional and modern basement floor insulation techniques:
Traditional Methods:
Fiberglass Batts: Fiberglass batts are a common choice for insulating basement walls but can also be used for insulating floors. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, making them a popular option for DIY projects.
Foam Board: Extruded or expanded polystyrene foam boards are another traditional insulation option for basement floors. They offer good thermal resistance and moisture resistance when installed correctly.
Modern Techniques:
Rigid Foam Insulation: Rigid foam insulation, such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS), is a popular choice for modern basement floor insulation. It provides excellent thermal performance, moisture resistance, and durability.
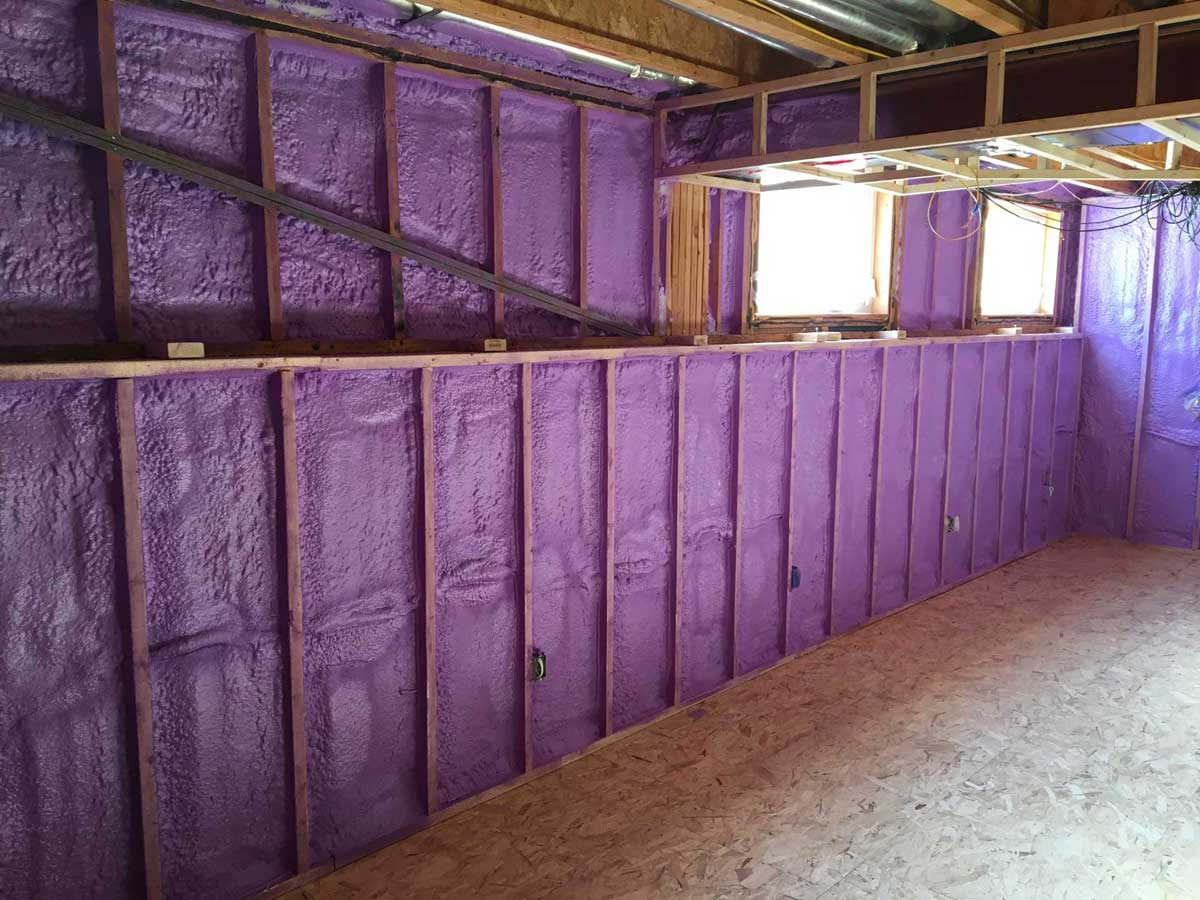
Spray Foam Insulation: Spray foam insulation offers superior air sealing properties and can be applied seamlessly to irregular surfaces, making it ideal for basement floors with complex layouts. It provides high R-value per inch and effectively fills gaps and cracks to prevent air leakage.
Considerations:
Cost: Traditional insulation methods like fiberglass batts may be more budget-friendly upfront, but modern techniques like spray foam insulation often provide better long-term value due to their superior performance and energy savings.
Moisture Resistance: Modern insulation materials like rigid foam and spray foam offer better moisture resistance compared to traditional options, helping prevent mold and mildew growth in the basement.
Installation Complexity: While traditional insulation methods are relatively straightforward to install, modern techniques may require professional expertise, especially for spray foam insulation, which involves specialized equipment and techniques.
Step-by-Step Guide to Insulating Your Basement Floor
Insulating your basement floor is a manageable DIY project that can yield significant energy savings and comfort improvements. Follow these step-by-step instructions to insulate your basement floor effectively:
Prepare the Surface: Start by cleaning the basement floor to remove any debris, dust, or moisture. Repair any cracks or uneven surfaces to ensure a smooth and level base for insulation installation.
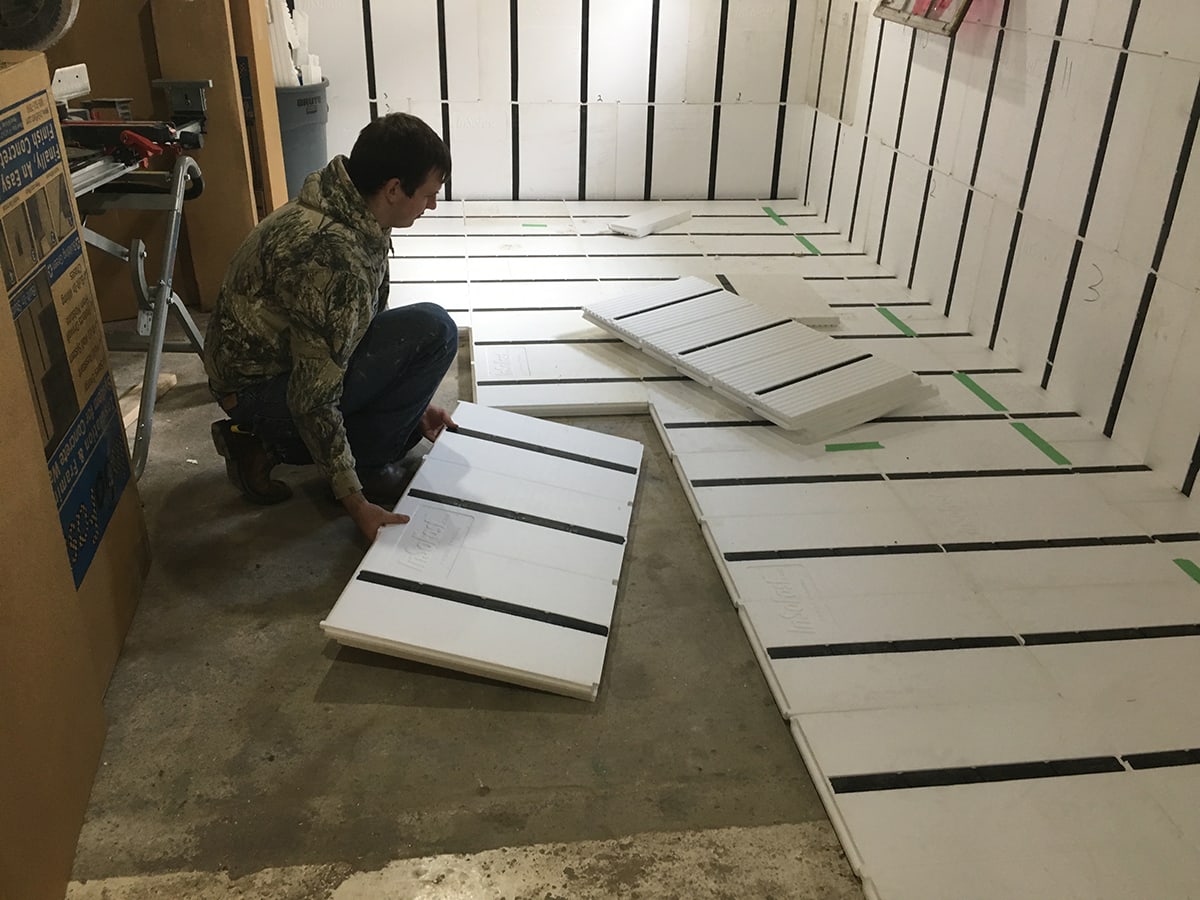
Choose the Insulation Material: Select the appropriate insulation material for your basement floor. Consider factors such as R-value, moisture resistance, and installation method. Common options include rigid foam insulation, spray foam insulation, and fiberglass batts.
Measure and Cut Insulation Panels: Measure the dimensions of your basement floor and cut the insulation panels to fit snugly within the perimeter walls. Use a utility knife or a saw to make precise cuts.
Install the Insulation: Place the insulation panels on the basement floor, starting from one corner and working your way across the entire surface. Ensure that the panels are tightly fitted together and that there are no gaps or overlaps.
Seal the Joints and Edges: Use tape or caulk to seal the joints and edges of the insulation panels, creating an airtight barrier against moisture and air infiltration. Pay special attention to areas where the insulation meets the walls and around utility penetrations.
Finish the Floor Surface: Once the insulation is installed and sealed, you can finish the basement floor surface according to your preferences. Options include installing carpet, laminate, vinyl, or tile flooring, depending on your design aesthetic and functional needs.
Materials and Tools Needed for Effective Basement Floor Insulation
Insulating your basement floor requires the right materials and tools to ensure a successful installation. Here’s what you’ll need:
Materials:
Insulation Panels: Choose rigid foam insulation, spray foam insulation, or fiberglass batts based on your preferences and budget.
Tape or Caulk: Use tape or caulk to seal the joints and edges of the insulation panels for air and moisture control.
Floor Finish: Select flooring materials such as carpet, laminate, vinyl, or tile to cover the insulated basement floor surface.
Tools:
Utility Knife or Saw: Use a utility knife or saw to cut insulation panels to the desired dimensions.
Tape Measure: Measure the dimensions of your basement floor accurately to ensure a proper fit for the insulation panels.
Safety Gear: Wear gloves, safety glasses, and a dust mask when handling insulation materials to protect yourself from irritation and exposure.
Caulking Gun: Use a caulking gun to apply caulk along the joints and edges of the insulation panels for sealing.
Installation Accessories: Depending on the insulation method chosen, you may need additional accessories such as fasteners, adhesives, or spray foam applicators.
Before starting your basement floor insulation project, gather all the necessary materials and tools to ensure a smooth and efficient installation process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Insulating Basement Floors
Insulating basement floors is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can compromise the effectiveness and durability of the insulation. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
Neglecting Moisture Management: Failure to address moisture issues before insulating the basement floor can lead to mold, mildew, and structural damage over time. Ensure that the basement is adequately waterproofed and that any existing moisture problems are addressed before installing insulation.
Using the Wrong Insulation Material: Choosing the wrong insulation material for your basement floor can result in poor thermal performance, moisture problems, or compatibility issues with the flooring material. Consider factors such as R-value, moisture resistance, and installation method when selecting insulation.
Incomplete Air Sealing: Insufficient air sealing around the edges and joints of insulation panels can lead to air leakage, reducing the effectiveness of the insulation and increasing energy bills. Use tape or caulk to seal all gaps and cracks for an airtight barrier.
Improper Installation: Rushing through the installation process or skipping important steps can result in uneven insulation coverage, gaps, or voids that compromise performance. Follow manufacturer instructions carefully and take the time to ensure proper installation.
Ignoring Building Codes and Regulations: Basement floor insulation projects may be subject to building codes and regulations that dictate insulation requirements, vapor barriers, and fire safety measures. Familiarize yourself with local codes and obtain necessary permits before starting work.
Overlooking Floor Finish Compatibility: Certain insulation materials may require specific types of flooring or floor finishes for compatibility and optimal performance. Consider how the chosen insulation method will affect the installation and performance of your desired floor finish.
GreenSpec: Housing Retrofit: Ground Floor Insulation
How-to install a wood subfloor over concrete RONA
INSULATING CONCRETE FLOORS – Extreme How To
INSULATING A CONCRETE SLAB – DIY Garage Conversion Floating Floor
How to Insulate a Basement Properly – The Options – Ecohome
Rigid Foam Insulation Installed over Existing Foundation Slabs
Best Practices For Insulating Your Basement With Spray Foam – Eco
Related Posts: