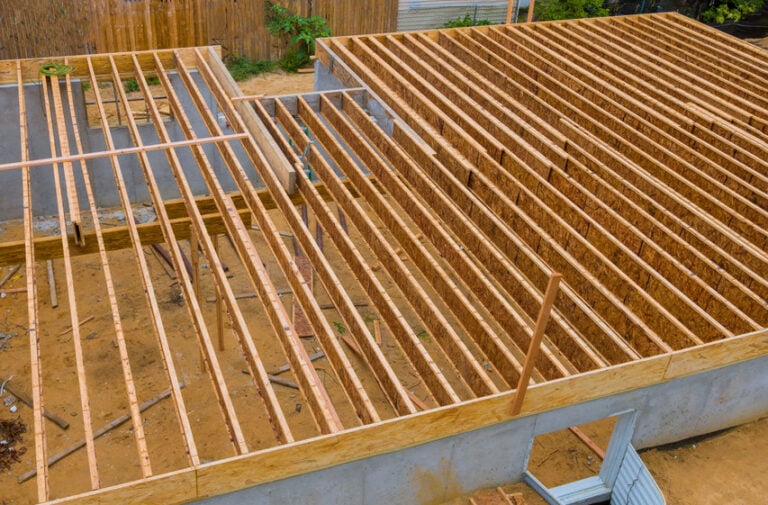
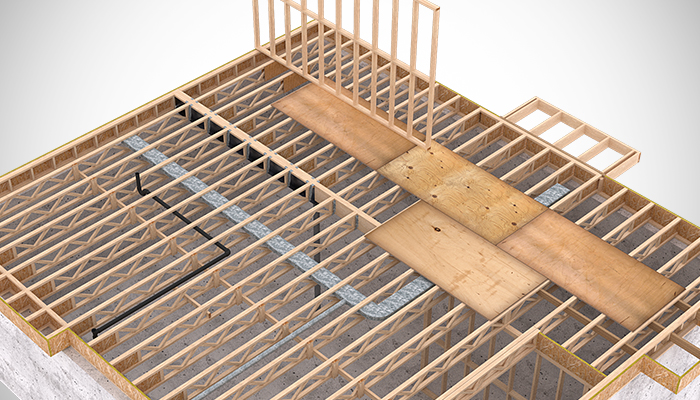
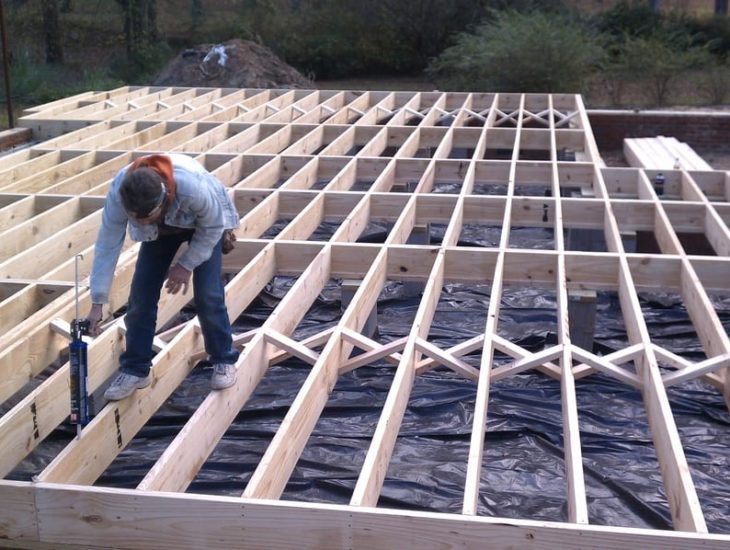
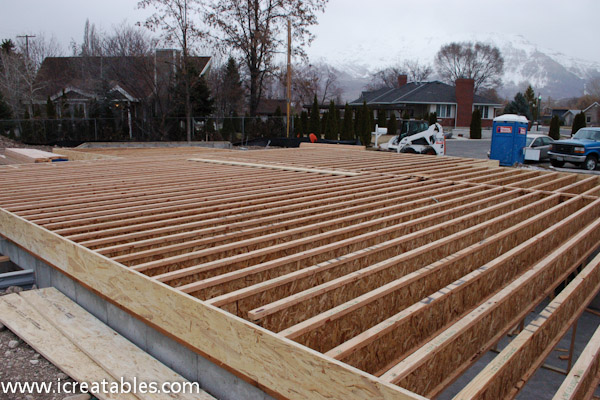
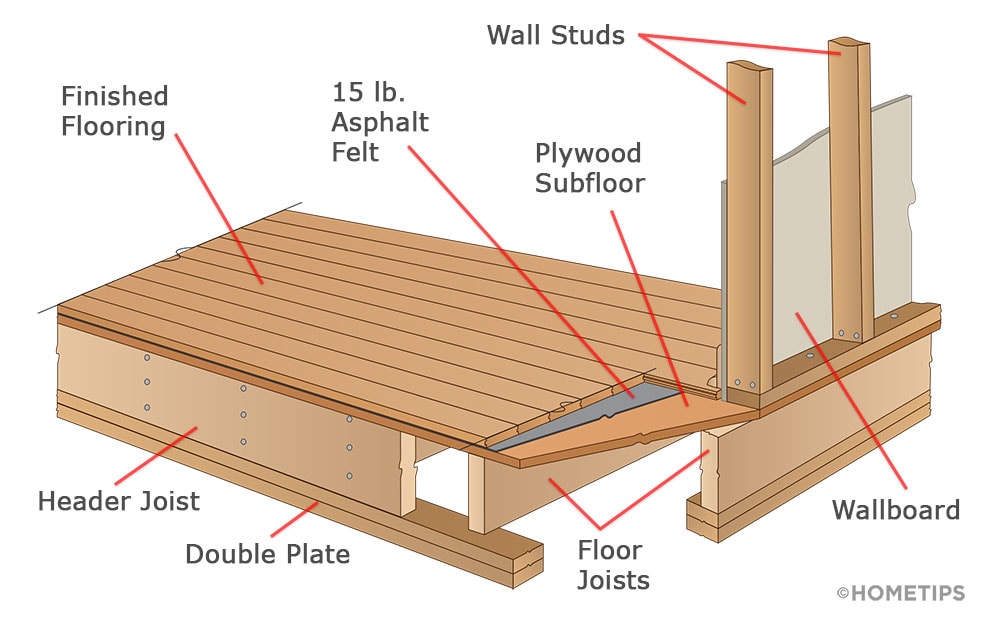
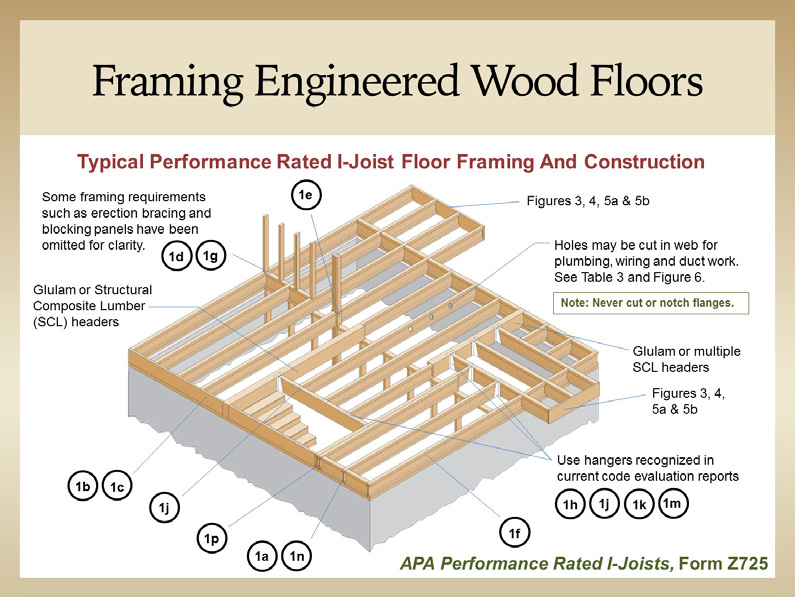
Wood floor joist construction is a fundamental aspect of building sturdy and reliable flooring systems in both residential and commercial structures. Floor joists are horizontal structural elements that support the weight of the floor above and any loads that will be placed upon it. Typically made from lumber, these joists span the gaps between the foundation walls, beams, or girders, forming a framework that distributes weight evenly and provides structural integrity. The spacing, size, and type of wood used for the joists are critical factors that influence the strength and performance of the flooring system. Standard lumber sizes for joists include 2×8, 2×10, and 2×12, with the dimensions selected based on the span they need to cover and the load requirements.
Images about Wood Floor Joist Construction
Wood Floor Joist Construction
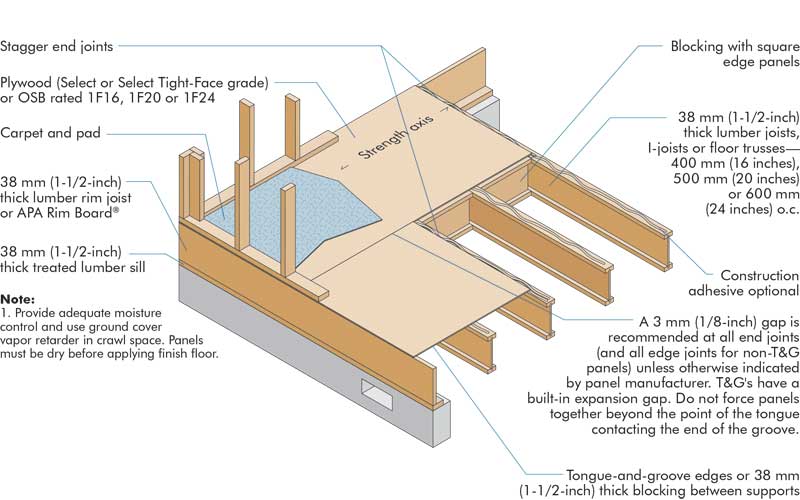
One of the key considerations in wood floor joist construction is the spacing between joists. Common spacing intervals are 12, 16, and 24 inches on center (OC), with 16 inches OC being the most typical in residential construction. Closer spacing provides greater strength and less deflection, which is particularly important for areas that will support heavy loads or require additional stability, such as kitchens or living rooms with large furniture. The choice of spacing is influenced by several factors, including the type of flooring to be installed on top, the anticipated load, and the overall design of the building. Engineers and builders must carefully calculate these factors to ensure that the floor system will be both safe and functional.
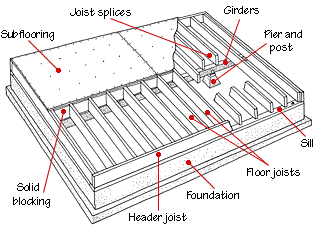
The type of wood used for floor joists also plays a crucial role in the construction process. Commonly used wood species include Douglas fir, southern pine, and spruce, each offering different strengths and characteristics. For example, Douglas fir is prized for its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to warping, making it a popular choice for joists. Engineered wood products, such as I-joists and laminated veneer lumber (LVL), are also frequently used in modern construction. These products offer superior strength and consistency compared to traditional solid wood joists, and they can span longer distances without sagging. Additionally, engineered wood joists are less susceptible to the natural imperfections and variations found in solid wood, providing a more uniform and predictable performance.
Proper installation techniques are essential for ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of wood floor joist systems. Joists must be securely fastened to the supporting structures, such as beams and girders, using metal hangers, nails, or screws specifically designed for structural applications. Ensuring that joists are level and properly aligned is critical, as any deviations can lead to uneven floors and potential structural issues over time. Bridging or blocking, which involves installing additional support pieces between joists, can further enhance stability and reduce vibrations. Additionally, considerations for moisture control, such as using treated wood in areas prone to dampness or installing vapor barriers, are important to prevent rot and decay, thereby extending the lifespan of the flooring system.
What Are Floor Joists and How Do They Work? BigRentz
Build a Squeak-Free Floor – Extreme How To
Floor Joist Spans for Home Building Projects – Todayu0027s Homeowner
Engineered Floor Joists: Which Are Best For Your Application
A Guide To Choosing Your Floor Framing System – Pacific Homes
Wooden Floor Framing
Engineered Floor Joists vs 2X10 Lumber: Which is Better?
What Are Floor Joists – What Is A Floor Joist icreatables.com
How to Build a Floor for a House : 11 Steps (with Pictures
Back to Basics – APA u2013 The Engineered Wood Association
Related Posts:
- Grey Wood Flooring Bathroom
- Rustic White Wood Flooring
- Wide Plank Pine Wood Flooring
- Blue Grey Wood Flooring
- Light Wood Flooring Ideas
- Distressed Wood Flooring
- Acacia Wood Flooring
- Wood Flooring Design
- Kitchen Engineered Wood Flooring
- Wood Floor Care Guide
Introduction to Wood Floor Joist Construction
Wood floor joists are an essential component of any home build. They provide the structural support for the entire floor system, which includes the subfloor, floor covering, and walls. Joists are typically made of lumber, but steel joists are becoming increasingly popular due to their strength and durability. When it comes to wood floor joists, there are many different types and sizes available, and they must be properly constructed and installed in order to ensure a strong, stable floor. In this article, we will take a look at some of the basics of wood floor joist construction and discuss some common questions related to this topic.
Types of Wood Floor Joists
There are two main types of wood floor joists: engineered and solid wood. Engineered joists are made from layers of wood that are pressed together under pressure into a single piece. They are usually thinner than solid wood joists, but they are often stronger and more flexible than solid wood. Solid wood joists are made from full-thickness lumber and usually require more support than engineered joists.
When it comes to selecting the correct type of joist for a particular project, it is important to consider the type of load being applied to the floor system, as well as the overall size of the space being constructed. While engineered joists may be better suited for smaller spaces or lighter loads, solid wood joists may be necessary for larger spaces or heavier loads.
Size Considerations for Wood Floor Joists
The size of the joist will also vary depending on the type of load being applied to the floor system. It is important to ensure that the joist is large enough to support the weight being applied without bending or sagging over time. The size of the joist should also be considered in relation to its span – that is, how far apart it will be spaced from support beams or walls. Generally speaking, wider spans require larger joists to provide adequate support.
Joist Spacing & Overhangs
The spacing between each joist should also be taken into consideration when constructing a wood floor system. Typically, joists should be spaced no more than 24 inches apart for residential applications; however, this can vary depending on the type of load being applied and the span between supports. Additionally, it is important to ensure that each joist is properly supported at both ends, either by a support beam or wall. It is also common practice to provide an overhang or cantilever beyond each support beam or wall; this helps to distribute the weight more evenly across all of the joists and prevents them from bending or sagging over time.
Installation of Wood Floor Joists
Once the size, type, and spacing of the joists have been determined, it is time to start installing them into the floor system. This process typically begins with attaching them to either a support beam or wall using hangers or other hardware. Once all of the joists have been secured in place, it is important to make sure that they are level and plumb before continuing with installation of the subfloor and other components of the floor system. Additionally, it is important to check that all connections between the joists and supports are secure and free from any movement or gaps; this will help ensure that your floor system remains stable over time.
What type of lumber should I use for my wood floor joists?
The type of lumber used for your wood floor joists will depend on several factors such as the size and type of load being applied to your floor system as well as your budget. Generally speaking, most residential applications will use either dimensional lumber or engineered lumber such as LVL (laminated veneer lumber). Dimensional lumber is typically less expensive but may require additional reinforcement if used for heavier loads or longer spans; engineered lumber is usually stronger but can also be more expensive.