Understanding Concrete Floor R-Value
Concrete floors are a popular choice in many buildings due to their durability and versatility. However, one important factor that often gets overlooked is the R value of concrete floors. R value refers to the ability of a material to resist heat flow, and it plays a crucial role in determining the energy efficiency of a building. Understanding the R value of concrete floors is essential for ensuring optimal thermal performance and reducing energy costs.
- Concrete’s R-value measures its ability to resist heat flow. Higher R-values indicate better insulating abilities.
- R-value is important for energy efficiency. High R-value floors retain heat in winter and stay cool in summer.
- Concrete’s low R-value around 0.5 per inch can lead to temperature discomfort and higher energy bills.
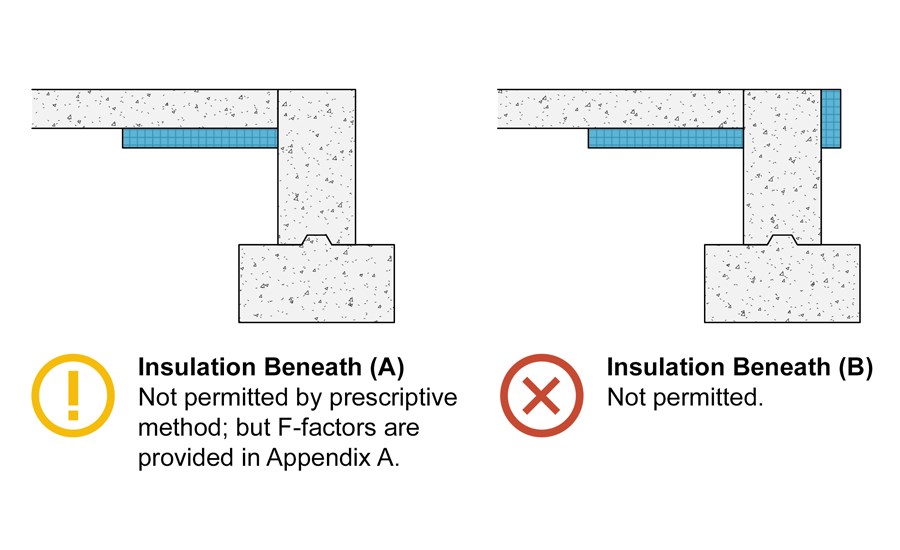
- Adding insulation beneath or within concrete can increase the total R-value to the recommended levels.
- Understanding concrete’s R-value helps create comfortable, energy-efficient building designs.

Factors Affecting Concrete Floor R Value
Several factors can affect the R value of a concrete floor. One of the most significant factors is the thickness of the concrete. Thicker concrete floors generally have a higher R value because they offer more resistance to heat flow. Additionally, the type and amount of insulation used in conjunction with the concrete can greatly impact its R value. Insulation materials such as foam boards or spray foam can significantly improve the thermal performance of a concrete floor.
- Concrete’s components impact its R-value. Dense aggregates like stone reduce R-value compared to lighter ones.
- Water content also affects R-value. Drier concrete resists heat flow better than wetter mixes.
- Concrete density influences R-value. Higher density means lower insulation ability. Lightweight concrete has higher R-value.
- Curing method impacts R-value. Moist-cured concrete may have lower R-value than concrete cured with blankets.
- Adding insulative materials like foam insulation boards increases total R-value. Polystyrene and polyurethane are common options.
Strategies for Improving the R Value of Concrete Floors
Although concrete floors have a relatively low R value, several strategies can be employed to improve their thermal performance. One effective strategy is to add insulation under the concrete slab. This can be done by installing rigid foam boards or spray foam insulation. By adding insulation beneath the concrete, the R value of the floor can be significantly increased.
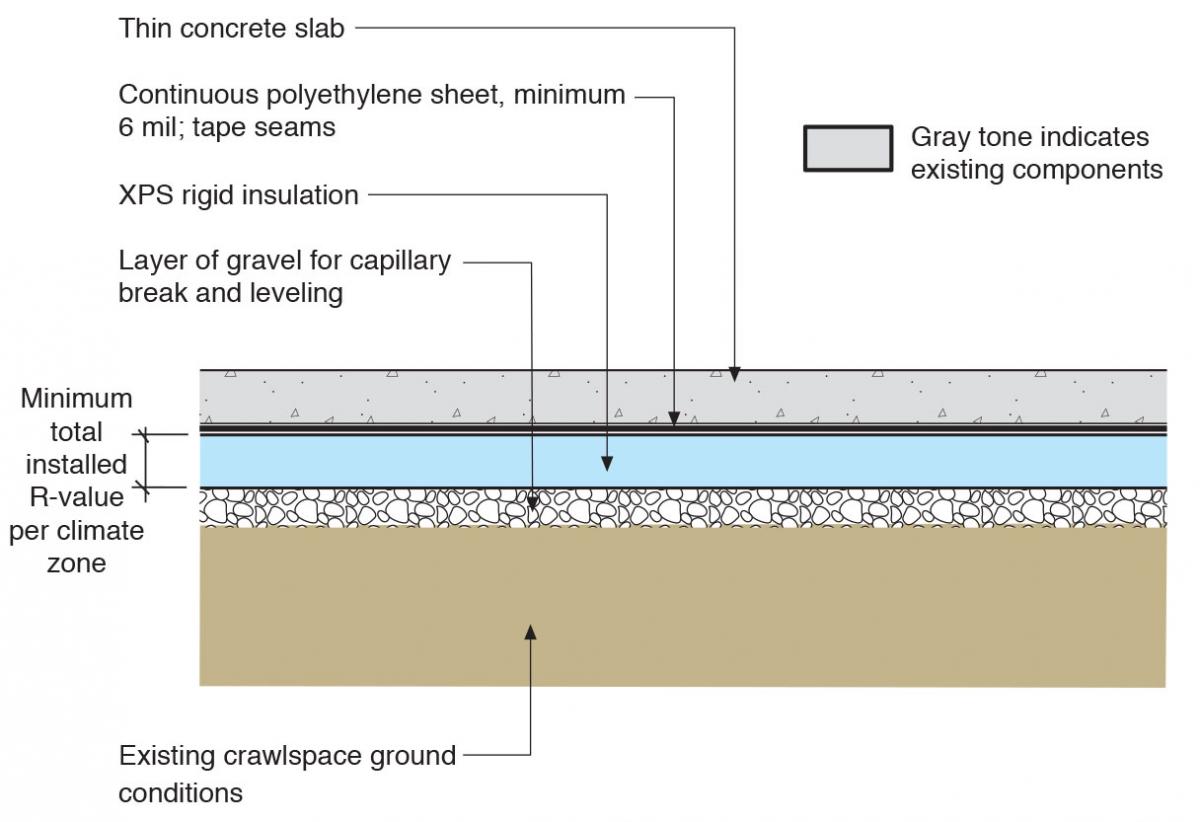
- Adding insulative underlayment beneath the slab increases the total R-value. Extruded polystyrene or rigid foam boards work well.
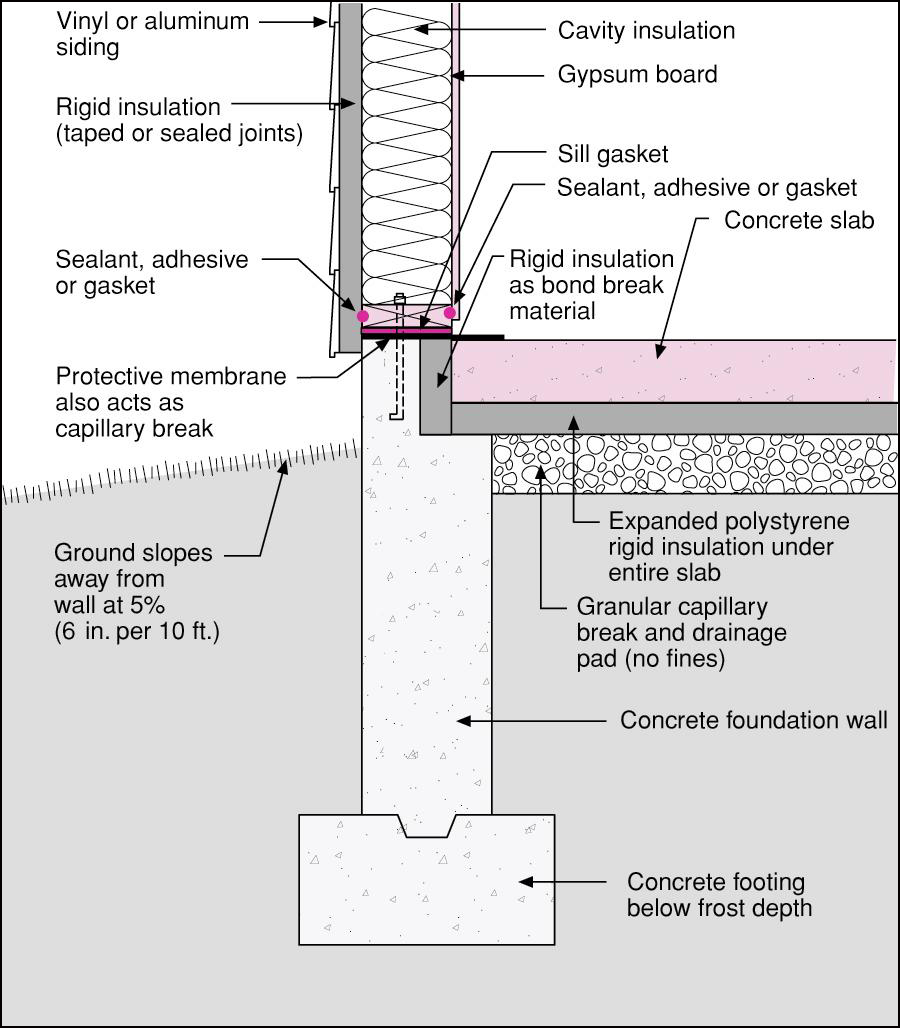
- Insulating concrete forms (ICFs) have built-in insulation, increasing wall and edge R-values.
- Insulated concrete blocks have polystyrene cores for higher R-value than standard blocks.
- Insulating concrete with additives like vermiculite and perlite creates air pockets, raising R-value.
- Pouring a cap of lightweight insulating concrete over standard concrete creates a cover with higher R-value.
Choosing the Right Products for Optimal R Value
When aiming to improve the R value of concrete floors, it is crucial to choose the right products and materials. High-quality insulation materials, such as closed-cell foam boards or spray foam, should be chosen to maximize the thermal performance. Additionally, selecting a concrete mix with a lower thermal conductivity can also help to improve the R value.
- Extruded polystyrene (XPS) boards provide R-5+ per inch. Moisture-resistant for below-grade use.
- Expanded polystyrene (EPS) boards are less dense than XPS. Offer R-4 per inch. Cost-effective.
- Polyurethane boards give very high R-value, 6-8 per inch. Can be applied directly under slab.
- Spray foam lets concrete be insulated without underlayment. Polyurethane foams provide R-6+ per inch.
- Fiberglass batts are ineffective under slabs due to moisture but may work between basement floor joists.
How Concrete Floor R Value Impacts Heating, Cooling, and Energy Costs
The R value of concrete floors plays a significant role in the heating, cooling, and overall energy costs of a building. A concrete floor with a low R value allows heat to escape or enter the building more easily, leading to increased energy consumption and higher heating or cooling costs. Conversely, a concrete floor with a higher R value provides better insulation, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling and resulting in lower energy costs.
- High R-value concrete floors reduce heat loss through slabs, decreasing heating costs in winter.
- Better insulation keeps interiors cooler in summer, reducing AC costs. In hot climates, reflectivity also helps.
- Insulated floors provide greater comfort by maintaining more consistent temperatures underfoot.
- Energy savings from insulated slab floors depend on climate. Cooler regions save more on heat; warmer ones on cooling.
- Added insulation costs are usually recouped over time through energy bill reductions. Thermal efficiency also rises.
Know Your R-Value The House Designers
Calibration of R-value of the existing floor assembly using
Insulation for Existing Crawl Space Floors Building America
Slab Edge Insulation Building America Solution Center
Below-Grade Insulation
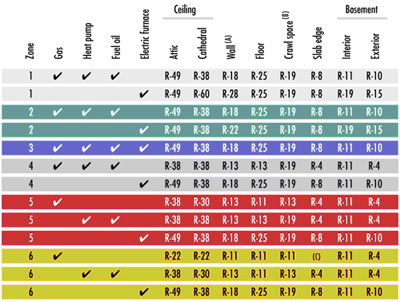
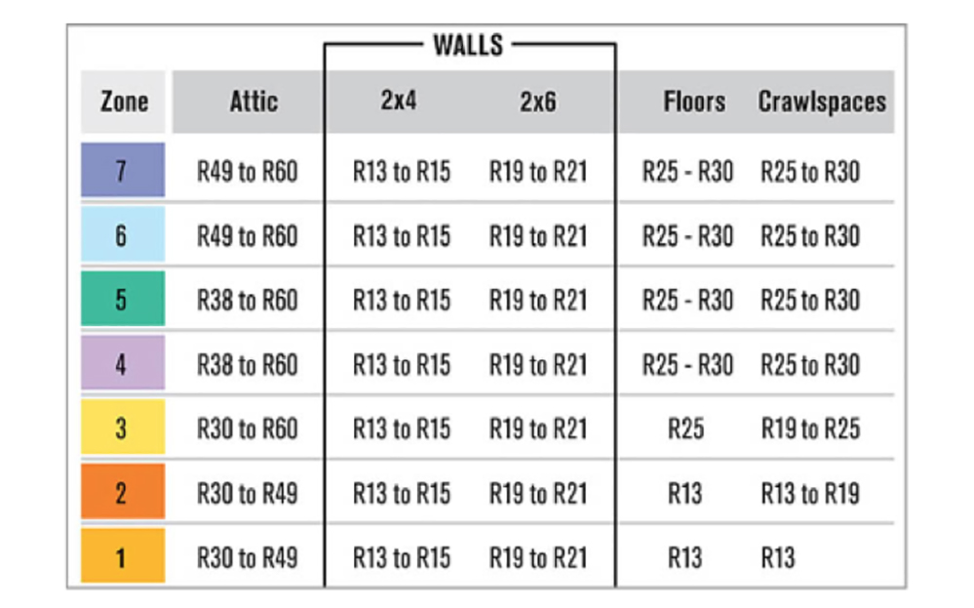
Insulation Levels for Cold, Hot and Moderate Climates
R-values for common construction types Building Performance
Radiant Floor Heat Healthy Heating
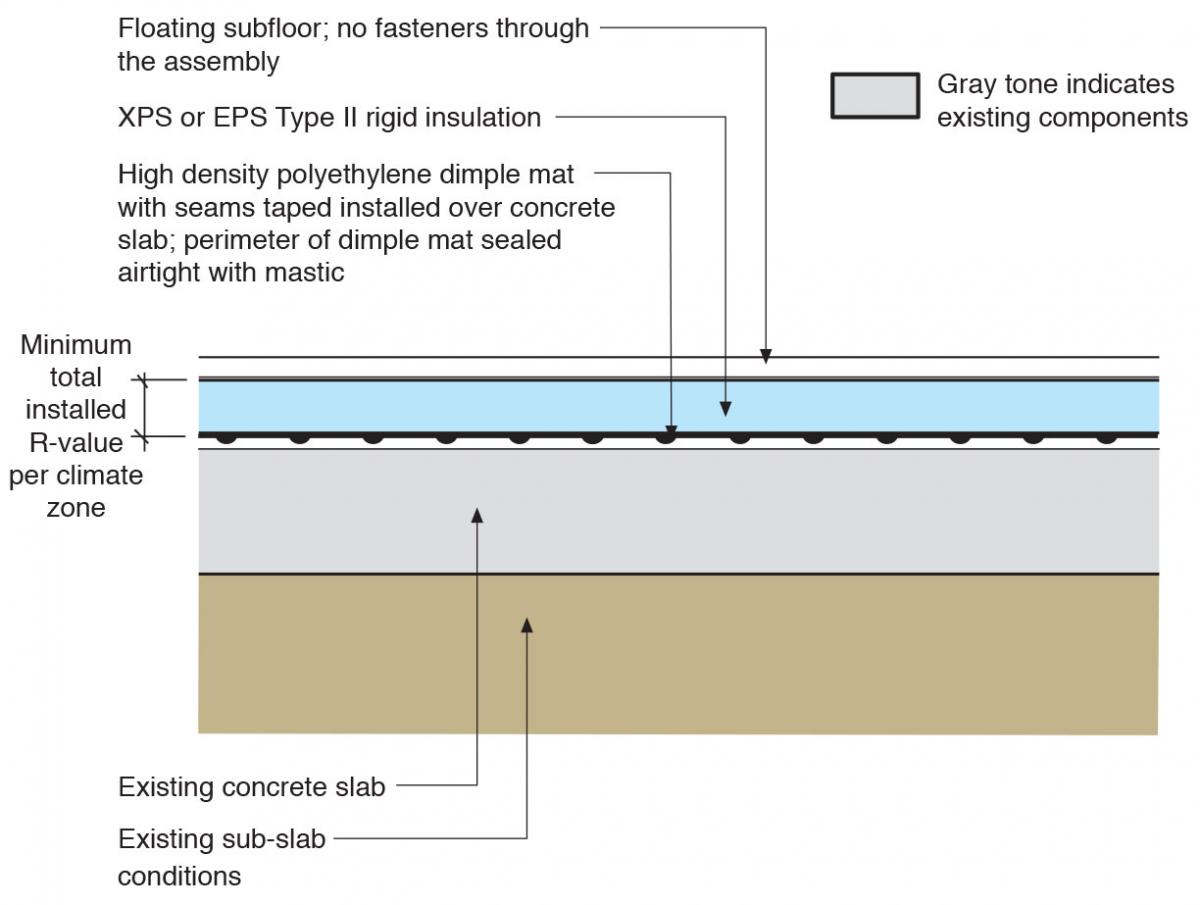
Rigid Foam Insulation Installed over Existing Foundation Slabs
Related Posts:
- Applying Concrete Floor Paint
- Non Slip Concrete Floor Sealer
- How To Paint Concrete Garage Floor
- Outdoor Concrete Floor Ideas
- Concrete Floor Covering Ideas
- Cracks In Polished Concrete Floors
- Drylok Concrete Floor Paint Colors
- Polished Concrete Floor Thickness
- Residential Stained Concrete Floors
- Cheap Concrete Floor Finishes