Designing a concrete floor slab involves a comprehensive process that considers various factors to ensure structural integrity, durability, and functionality. A concrete floor slab serves as the foundation for buildings and structures, supporting the weight of occupants, furniture, equipment, and other loads. The design of a concrete floor slab begins with determining the specific requirements of the project, including the intended use of the space, the anticipated loads, and the environmental conditions. Once these factors are established, engineers and architects can proceed with the design process, which typically involves several key steps.
Images about Concrete Floor Slab Design Guide
Concrete Floor Slab Design Guide
The first step in designing a concrete floor slab is to determine the thickness of the slab based on the anticipated loads and the soil conditions at the site. The thickness of the slab will vary depending on factors such as the type of building, the size of the space, and the type of concrete used. Engineers use structural analysis and design software to calculate the required thickness of the slab, taking into account factors such as dead loads (the weight of the slab itself) and live loads (the weight of occupants and other movable loads).
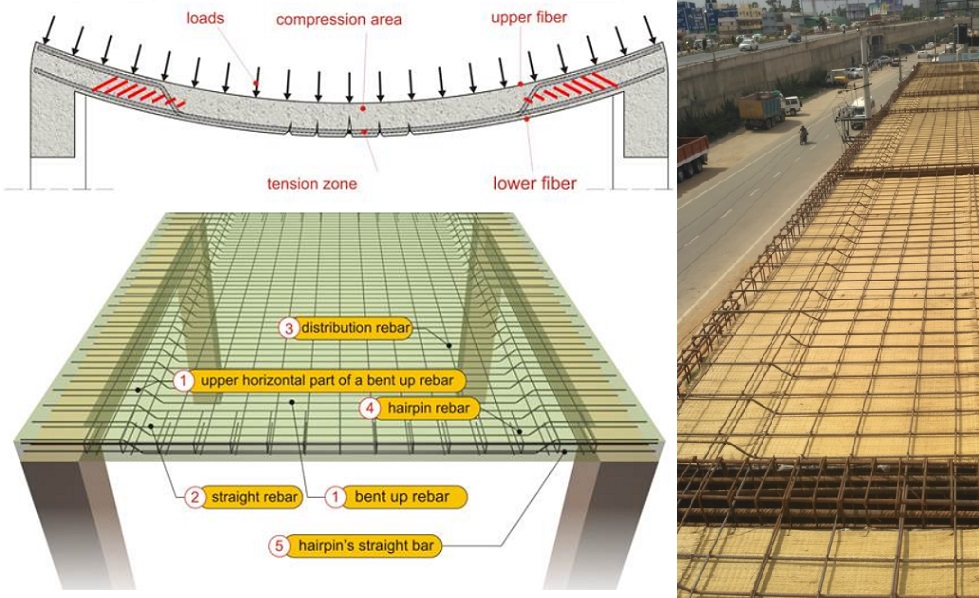
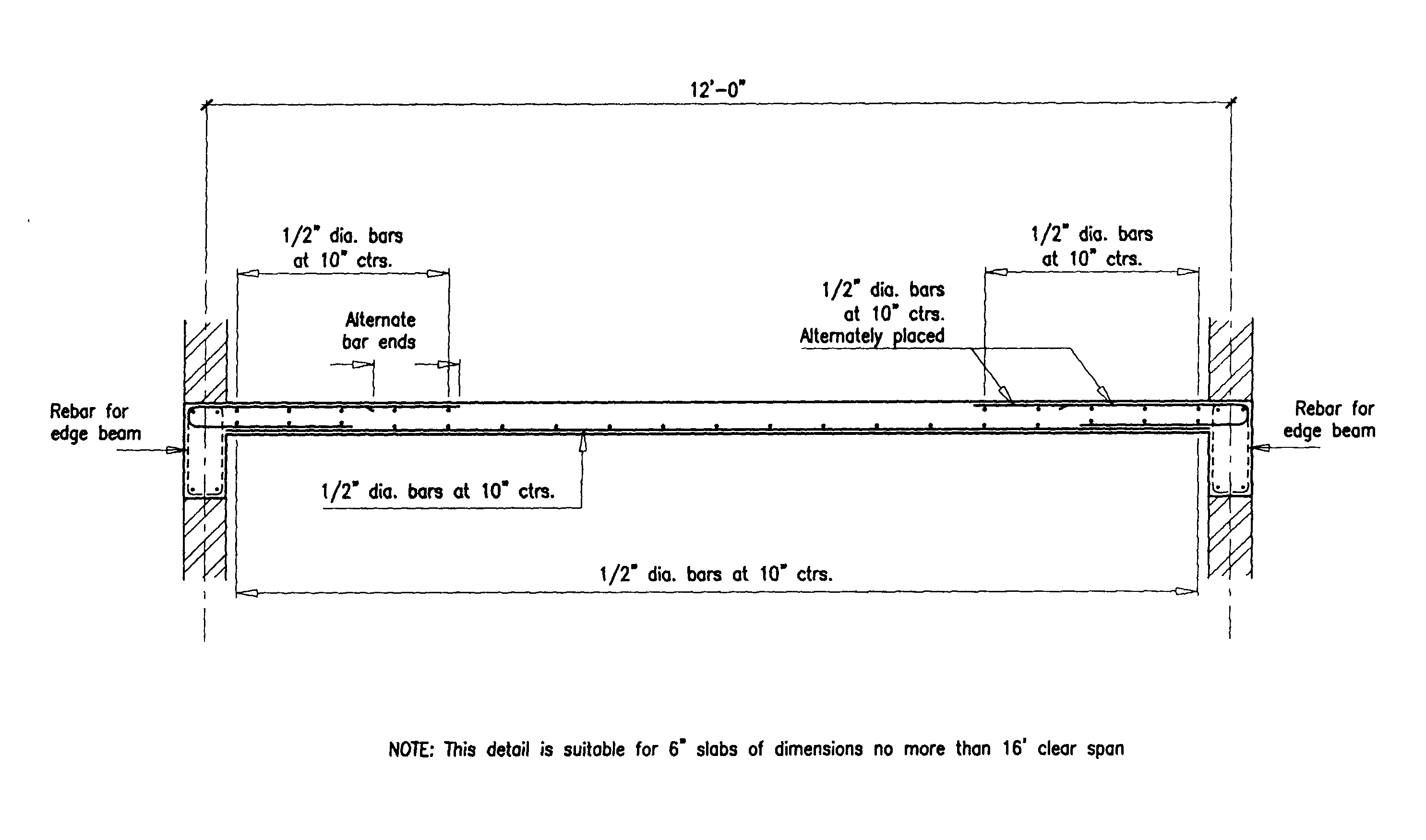
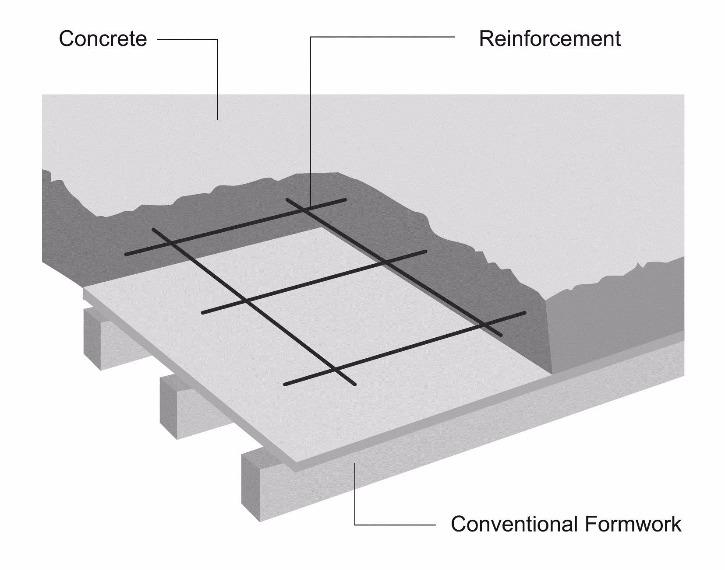
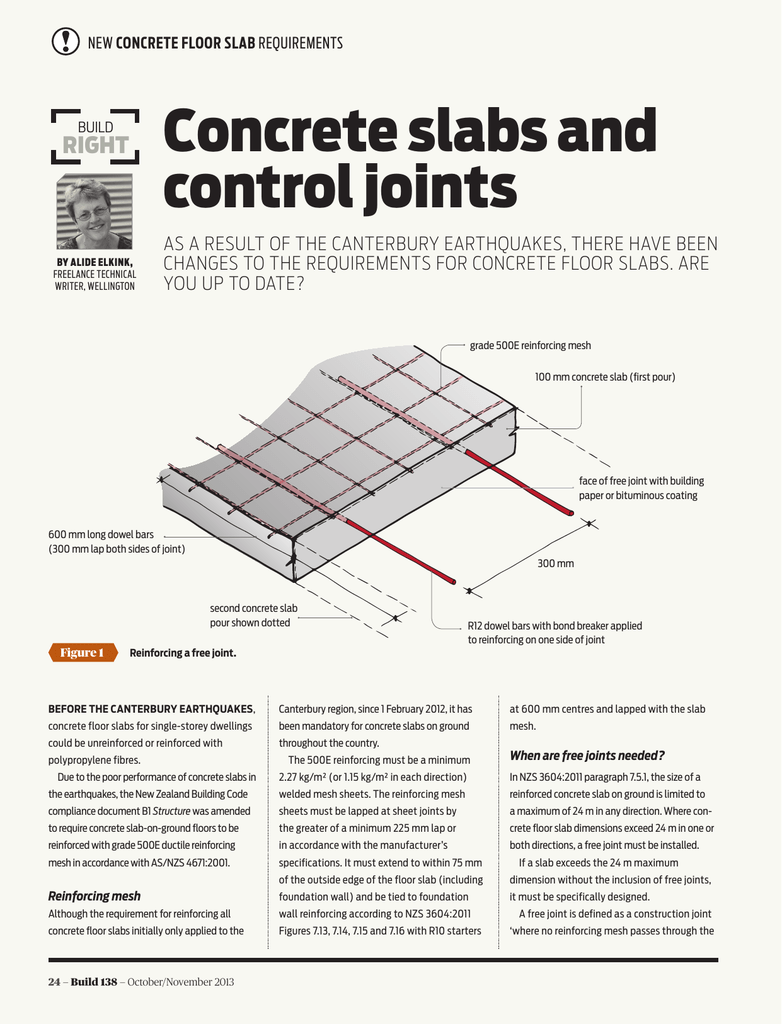
After determining the thickness of the slab, engineers proceed with designing the reinforcement for the slab to ensure its structural integrity and resistance to bending and cracking. Reinforcement typically consists of steel bars or mesh embedded within the concrete to provide additional strength and support. The spacing and size of the reinforcement bars are carefully calculated based on the anticipated loads and the dimensions of the slab. Engineers also consider factors such as expansion joints, which are used to control cracking caused by temperature changes and shrinkage during the curing process.
Once the design of the concrete floor slab is complete, engineers create detailed construction drawings and specifications that outline the requirements for the slab, including materials, dimensions, reinforcement details, and construction methods. These documents serve as a guide for contractors and construction crews during the installation process, ensuring that the slab is constructed according to the design specifications and meets the required standards for strength, durability, and safety.
Throughout the design and construction process, engineers and architects work closely with contractors, suppliers, and other stakeholders to ensure that the concrete floor slab meets the specific requirements of the project and complies with building codes and regulations. By carefully considering factors such as loads, soil conditions, reinforcement, and construction methods, designers can create concrete floor slabs that provide a stable and durable foundation for buildings and structures, ensuring their long-term performance and functionality.
Reinforced Concrete Slab Design Guidelines – The Constructor
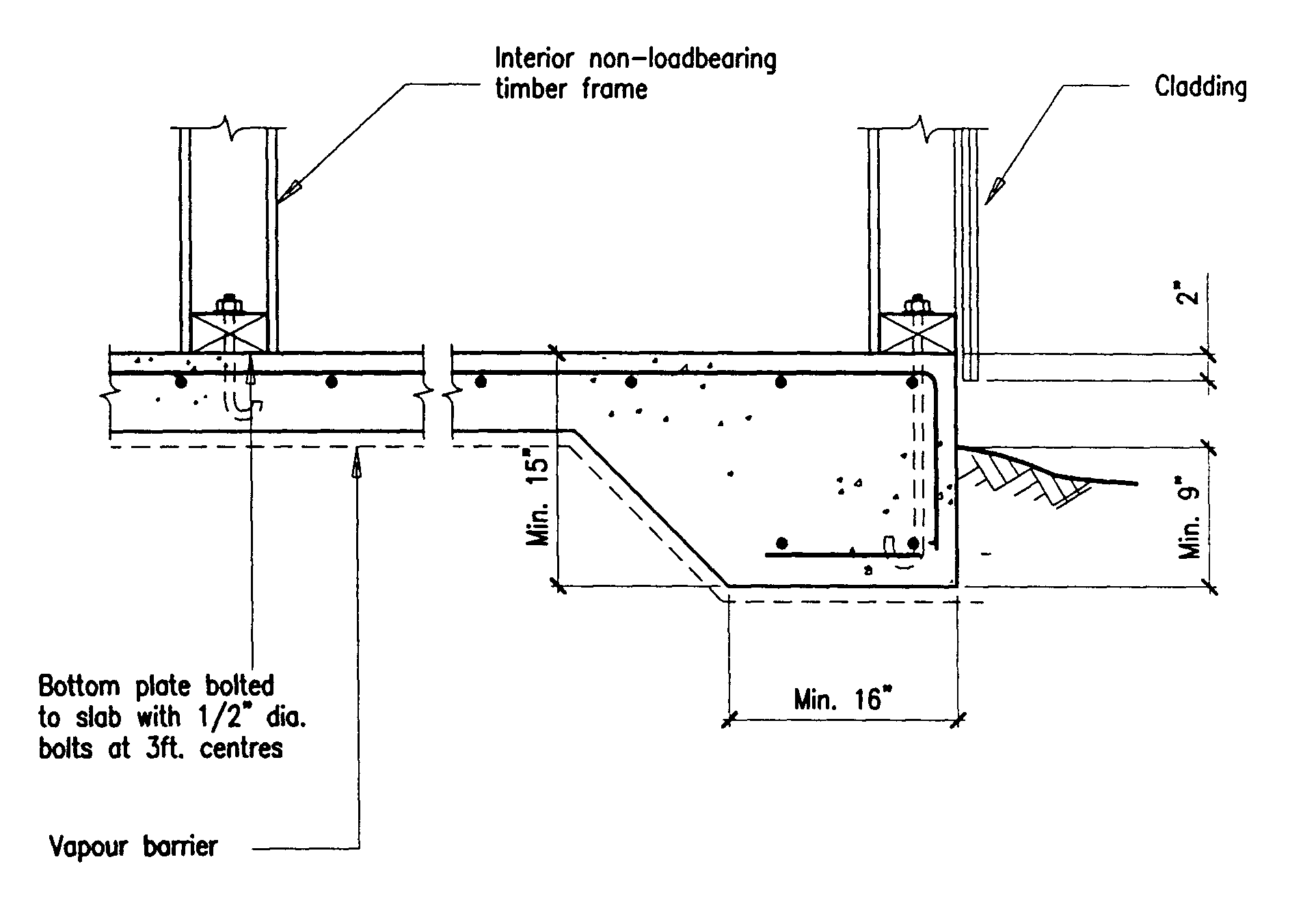
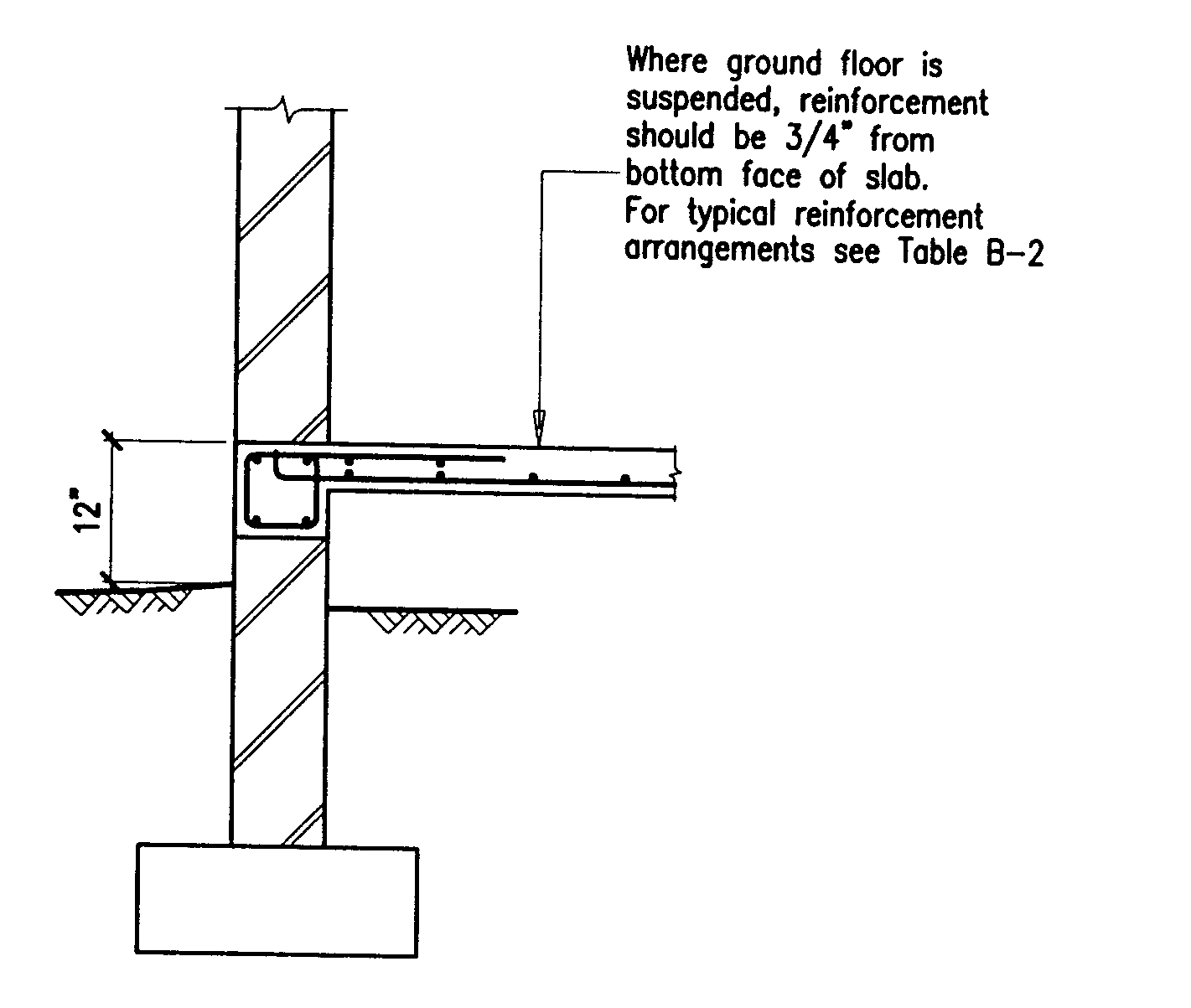
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
Building Guidelines Concrete Floors, Slabs
How to Design One-way Slab as per ACI 318-19? Example Included
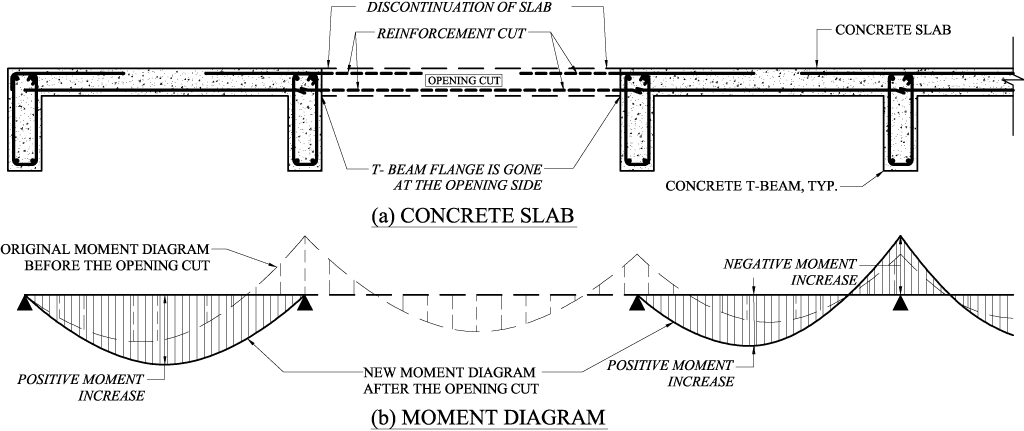
STRUCTURE magazine Creating an Opening in Existing Floors
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
Floor Slabs WBDG – Whole Building Design Guide
Working with Design of a Reinforcement Concrete Slab
The device reinforced concrete slab basement floor Download
Upper Floors
Related Posts:
- Applying Concrete Floor Paint
- Non Slip Concrete Floor Sealer
- How To Paint Concrete Garage Floor
- Outdoor Concrete Floor Ideas
- Concrete Floor Covering Ideas
- Cracks In Polished Concrete Floors
- Drylok Concrete Floor Paint Colors
- Polished Concrete Floor Thickness
- Residential Stained Concrete Floors
- Cheap Concrete Floor Finishes
Concrete floor slab design is an important factor in the construction of any building or structure. A properly designed concrete floor slab can provide a strong and durable foundation for any type of structure, while a poorly designed slab may lead to structural failure or costly repairs down the road. Designing a concrete floor slab requires knowledge of structural engineering, building codes, and other important considerations such as load-bearing requirements and drainage. This guide provides an overview of the design process and factors that must be taken into consideration when designing a concrete floor slab.
What is a Concrete Floor Slab?
A concrete floor slab is a flat, horizontal surface made from poured concrete that is typically used as the foundation for a building or other structure. Concrete slabs are often used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects as well as in outdoor areas such as patios and decks.
Load Bearing Requirements for Concrete Floor Slab Design
Before designing a concrete floor slab, it is important to consider the loads that will be placed on the slab. This includes the weight of the structure itself as well as any additional weight that may be applied during its use, such as furniture or equipment. The load-bearing requirements of the concrete floor slab should be determined based on the anticipated loads that will be placed on it over its lifetime.
Design Considerations for Concrete Floor Slab
When designing a concrete floor slab, several factors must be taken into consideration. These include:
Subgrade Preparation
Before pouring a concrete floor slab, it is important to prepare the subgrade beneath it. This includes removing any vegetation and loosening up the soil to ensure proper drainage and compaction. It is also important to level the soil before pouring the concrete to ensure an even surface and uniform thickness throughout the slab.
Reinforcement
The use of reinforcement in a concrete floor slab can help increase its strength and durability. Steel rebar or wire mesh can be used to reinforce the slab and prevent cracking due to changes in temperature or moisture. Reinforcement should be spaced evenly throughout the slab and securely embedded in it before the concrete is poured.
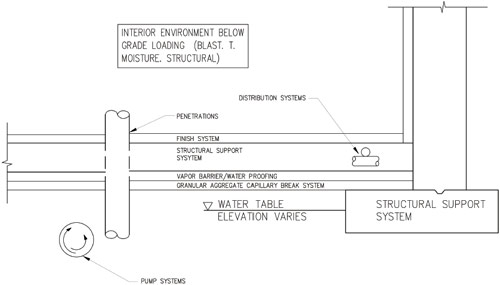
Drainage
Drainage is an important factor when designing a concrete floor slab. Poor drainage can lead to water accumulation beneath the slab which can cause cracking or heaving of the concrete. To ensure proper drainage and prevent pooling water beneath the slab, it should be designed with a slight slope towards drains or other outlets such as gutters or storm drains.
Curing
Once the concrete has been poured, it is important to allow it to cure properly before using it. Curing allows the concrete to gain strength over time by preventing evaporation from occurring too quickly. The curing process should take place over several days or weeks depending on climate conditions, with most concrete slabs taking about 28 days to fully cure.
What is a concrete floor slab?
A concrete floor slab is a flat, horizontal surface made from poured concrete that is typically used as the foundation for a building or other structure. It is often used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects as well as in outdoor areas such as patios and decks.
How do I determine the load-bearing requirements of my concrete floor slab?
The load-bearing requirements of your concrete floor slab should be determined based on the anticipated loads that will be placed on it over its lifetime. This includes the weight of the structure itself as well as any additional weight that may be applied during its use, such as furniture or equipment.
What are some design considerations for my concrete floor slab?
Several design considerations must be taken into account when designing a concrete floor slab. These include subgrade preparation, reinforcement, drainage, and curing. Subgrade preparation involves removing vegetation and loosening up soil for proper drainage and compaction, while reinforcement involves using steel rebar or wire mesh to strengthen the slab against cracking due to changes in temperature or moisture.