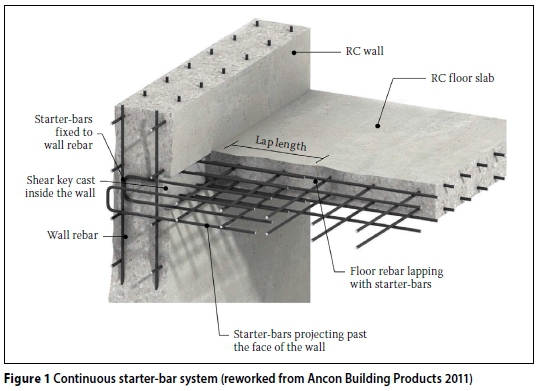
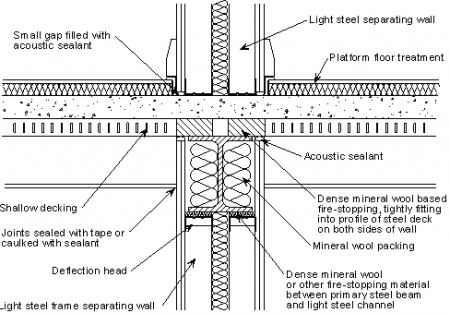
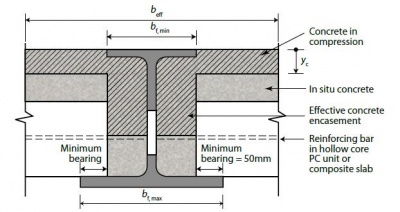
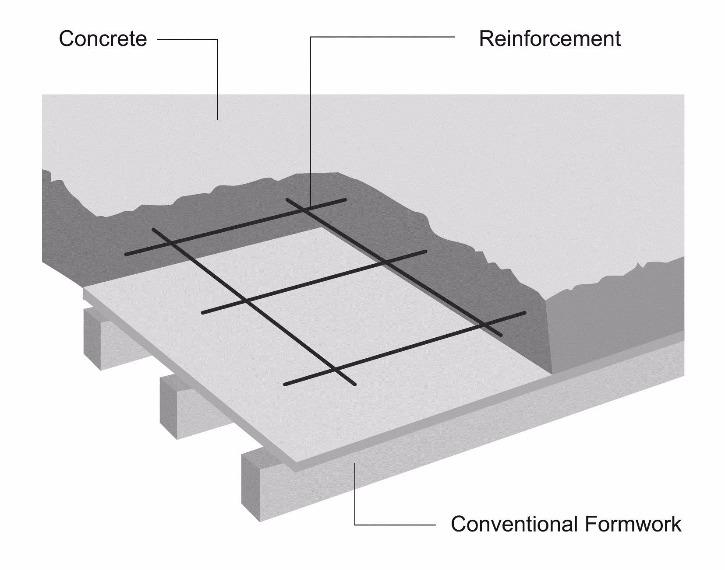
Reinforced concrete floor systems are widely used in construction due to their strength, durability, and versatility. These systems consist of a combination of steel reinforcement and concrete, resulting in a material that can withstand heavy loads, resist fire, and provide efficient support for various structures. Let’s explore the introduction to reinforced concrete floor systems, highlighting their advantages, types, and applications.
Advantages of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems:
Reinforced concrete floor systems offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in construction projects. Firstly, their high strength allows them to support heavy loads without excessive deflection or deformation. This makes them suitable for structures that require large open spaces, such as warehouses, industrial buildings, and parking garages.
Second, reinforced concrete floor systems have excellent fire resistance. The concrete acts as a thermal barrier, protecting the steel reinforcement from high temperatures. This property is crucial in buildings where fire safety is a priority, such as residential complexes, hospitals, and commercial spaces.
Additionally, these floor systems can be designed to provide acoustic insulation, reducing noise transmission between floors. This is particularly important in multi-story buildings, hotels, and educational institutions, where a peaceful and comfortable environment is essential.
Types of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems:
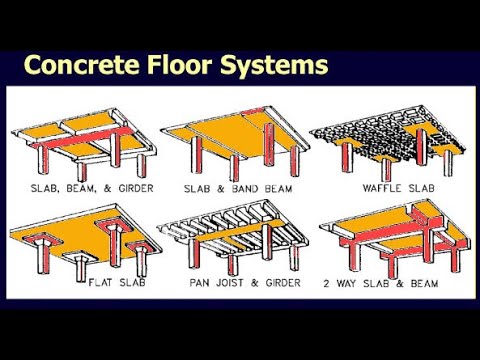
There are several types of reinforced concrete floor systems, each offering unique characteristics and advantages. One commonly used type is the flat plate system, where a continuous slab is supported directly by columns. This system provides simplicity in construction and allows for flexibility in floor layout.
Another type is the one-way joist system, which consists of parallel beams supporting a slab. This system is suitable for longer spans and offers efficient use of materials. It is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings.
The two-way joist system, also known as the waffle slab, features a grid of beams and joists that form a pattern of square or rectangular cells. This system provides increased stiffness and strength, making it ideal for heavy loads and long spans. It is commonly used in high-rise buildings and industrial structures.
Applications of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems:
Reinforced concrete floor systems find applications in various construction projects. In residential buildings, they are used to create safe and durable floors that can support the weight of furniture and occupants. The fire resistance of these systems adds an extra layer of safety, giving residents peace of mind.
In commercial buildings, reinforced concrete floor systems are used to create open and flexible spaces. The strength of the system allows for the construction of large, column-free areas, making it suitable for retail spaces, offices, and showrooms. The fire resistance and acoustic insulation properties are also advantageous in these settings.
Industrial buildings, such as factories and warehouses, benefit from the high load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete floor systems. Heavy machinery, storage racks, and vehicles can be accommodated without compromising the structural integrity of the floor. The fire resistance of these systems is crucial in industrial settings, where flammable materials may be present.
Benefits and Advantages of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems
Reinforced concrete floor systems offer numerous benefits and advantages over other flooring options. We will explore some of the key advantages of using reinforced concrete floor systems in construction projects.
High Load-Carrying Capacity
One of the primary benefits of reinforced concrete floor systems is their ability to support heavy loads. The combination of concrete and reinforcement materials ensures that the floor can withstand the weight of equipment, machinery, and even multiple levels of a building. This high load-carrying capacity makes reinforced concrete floor systems ideal for industrial and commercial spaces.
Fire Resistance
Another significant advantage of reinforced concrete floor systems is their excellent fire resistance. Concrete is inherently fire-resistant, and when combined with reinforcement materials, it becomes even more robust. This feature provides valuable protection in case of a fire, allowing occupants to evacuate safely and giving firefighters more time to control the situation.
Durability and Longevity
Reinforced concrete floor systems are known for their durability and longevity. When properly designed and constructed, these floors can last for decades with minimal maintenance. They are resistant to wear and tear, impact, and weathering, making them a reliable and cost-effective choice for long-term use.
Versatility in Design
Reinforced concrete floor systems offer design flexibility, allowing architects and engineers to create unique and aesthetically pleasing spaces. The versatility of reinforced concrete enables the construction of various floor shapes, including flat slabs, beams and slabs, and waffle slabs. This adaptability makes it easier to meet specific architectural and functional requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Reinforced concrete floor systems can contribute to sustainable building practices. Concrete is made from locally available materials, which reduces transportation costs and carbon emissions. Additionally, concrete has a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste generation. Furthermore, concrete has excellent thermal mass properties, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings.
Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial cost of reinforced concrete floor systems may be higher compared to some alternative flooring options, their long-term cost-effectiveness makes them an attractive choice. The durability, low maintenance requirements, and extended lifespan of these floors result in lower life-cycle costs, making them a wise investment in the construction industry.
Types of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems
Reinforced concrete floor systems come in various types, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Below are some of the most common types of reinforced concrete floor systems used in construction projects.
Flat Slabs
Flat slabs are a popular choice for buildings that require flexibility in space planning. They consist of a flat plate with thickened areas called drop panels at columns and load-bearing walls. Flat slabs offer simplicity in construction, efficient use of space, and flexibility for mechanical and electrical installations.
Beam and Slab Systems
Beam and slab systems, also known as conventional reinforced concrete slabs, are widely used in residential and commercial construction. They consist of a grid of beams supported by columns, with concrete slabs spanning between the beams. This system provides enhanced structural strength and allows for longer spans between columns.
Waffle Slabs
Waffle slabs, also known as two-way slabs, are suitable for buildings that require large unobstructed spans. They consist of a series of ribs forming a waffle-like pattern, with the concrete slabs spanning between the ribs. Waffle slabs offer high load-carrying capacity, improved strength-to-weight ratio, and reduced overall floor thickness.
Post-Tensioned Slabs
Post-tensioned slabs are a type of reinforced concrete floor system that utilizes post-tensioning cables to increase the overall strength and durability of the floor. These systems are commonly used in areas with large spans or where deflection control is critical. Post-tensioned slabs offer increased structural efficiency and flexibility in design.
Composite Slabs
Composite slabs combine steel beams and reinforced concrete to create a highly efficient and lightweight floor system. The steel beams provide the primary structural support, while the concrete acts as a composite material, enhancing the strength and stiffness of the floor. Composite slabs offer rapid construction, reduced dead load, and excellent fire resistance.
Design Considerations for Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems
The design of reinforced concrete floor systems requires careful consideration to ensure structural integrity, safety, and functionality. Let’s discuss some key design considerations that architects and engineers should keep in mind when designing reinforced concrete floors.
Load Requirements
The first step in designing a reinforced concrete floor system is determining the load requirements. This involves considering the intended use of the floor, the expected live loads, and any additional factors such as equipment, storage, or occupancy. By accurately assessing the loads, engineers can determine the appropriate floor thickness, reinforcement, and support system needed.
Deflection Control
Deflection control is crucial in reinforced concrete floor design to ensure occupant comfort and prevent structural issues. Excessive deflection can lead to cracking, sagging, or even failure of the floor. Engineers must carefully analyze and calculate the deflection limits based on the specific project requirements and applicable building codes.
Reinforcement Design
The reinforcement design plays a critical role in the structural integrity and load-carrying capacity of the floor system. Engineers must carefully determine the reinforcement layout, size, and spacing to ensure proper distribution of loads and resistance against bending and cracking. Factors such as concrete strength, environmental conditions, and construction methods should be considered when designing the reinforcement.
Construction Joints and Expansion Joints
Construction joints and expansion joints are essential elements in reinforced concrete floor design. Construction joints allow for the division of large floor areas into manageable sections during construction, while expansion joints accommodate the thermal and moisture-related movements of the floor. Proper placement and design of these joints are crucial to prevent cracking and ensure long-term durability.
Waterproofing and Vapor Barrier
Waterproofing and vapor barrier systems are critical in reinforced concrete floor design, especially in areas exposed to moisture or below-grade floors. These systems protect the floor from water penetration, preventing damage and deterioration. Proper selection and installation of waterproofing and vapor barrier materials are essential to maintain the integrity of the floor system.
Serviceability and Maintenance Considerations
In addition to structural considerations, engineers must also address serviceability and maintenance requirements in the design of reinforced concrete floor systems. This includes provisions for access, maintenance of utilities, ease of cleaning, and durability against wear and tear. By considering these factors, the design can optimize the functionality and longevity of the floor system.
Maintenance and Durability of Reinforced Concrete Floor Systems
Proper maintenance and regular inspections are essential to ensure the durability and longevity of reinforced concrete floor systems. Below are some key maintenance practices and considerations to help maximize the lifespan of these floors.
Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs of damage or deterioration in the reinforced concrete floor system. Inspections should include visual assessments, crack monitoring, and assessment of structural integrity. By detecting issues early on, appropriate repairs and maintenance can be implemented, preventing further damage and ensuring the safety of occupants.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning is important to maintain the aesthetics and functionality of the reinforced concrete floor system. Depending on the specific requirements, cleaning methods may include sweeping, mopping, or using specialized cleaning agents. Additionally, maintenance practices such as sealing, re-coating, or applying protective coatings can help enhance the durability and resistance of the floor.
Repairing Cracks and Spalling
Cracks and spalling are common issues in reinforced concrete floor systems, often caused by shrinkage, settlement, or external factors. It is crucial to address these issues promptly to prevent further deterioration and potential structural problems. Repair methods may include epoxy injection, crack stitching, or patching with compatible materials.
Moisture and Chemical Protection
Moisture and chemical exposure can significantly impact the durability of reinforced concrete floor systems. Proper moisture barriers, waterproofing, and chemical-resistant coatings should be applied to protect the floor from water penetration, chemical spills, and corrosion. Regular inspections and maintenance of these protective measures are essential to ensure their effectiveness.
Load Management
Managing the load on the reinforced concrete floor system is crucial to prevent overloading and excessive deflection. Regularly assess the load requirements, ensure that heavy equipment or storage is adequately supported, and avoid exceeding the recommended load limits. By properly managing the load, the floor system can maintain its structural integrity and longevity.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to harsh weather conditions can affect the durability of reinforced concrete floor systems. It is important to consider these factors during the design and maintenance processes. Insulation, proper ventilation, and the use of protective coatings can help mitigate the impact of environmental factors and extend the lifespan of the floor system.
Professional Maintenance and Repair
While regular inspections and maintenance can go a long way in preserving the durability of reinforced concrete floor systems, it is also important to engage professional maintenance and repair services when needed. Trained professionals have the knowledge and expertise to identify and address any underlying issues, ensuring that proper repair techniques are used and that the floor system is restored to its optimal condition.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining detailed documentation and records of the maintenance and repair activities performed on the reinforced concrete floor system is crucial. This includes keeping records of inspections, repairs, cleaning schedules, and any changes or modifications made to the floor system. These records can serve as a valuable reference for future maintenance and help in identifying any recurring issues or patterns.
Education and Training
Educating building owners, facility managers, and occupants about the proper care and maintenance of reinforced concrete floor systems is essential. This can include providing guidelines on cleaning techniques, load management, and the importance of regular inspections. Training programs can also be organized to ensure that maintenance staff are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to properly care for the floor system.
Life Cycle Cost Analysis
Performing a life cycle cost analysis is an important step in assessing the overall cost-effectiveness of reinforced concrete floor systems. This analysis takes into account the initial construction costs, maintenance and repair expenses, and the expected lifespan of the floor system. By considering the long-term costs and benefits, building owners can make informed decisions regarding the maintenance and replacement of the floor system.
Types of Cast-in-Place Concrete Roof and Floor Systems
Types of Economical Floor Systems for Reinforced Concrete Buildings
Floor systems – Steel Construction
Types of Economical Floor Systems for Reinforced Concrete Buildings
Concrete Floor Systems Dimensions
Applied variants of various floor systems made on: (a) a concrete
Upper Floors
Related Posts: