Diamond concrete flooring polishing provides consumers a number of options to modify the appearance of their floors. Beyond sweeping and scrubbing the floor, establish a substantial concrete floor care method which includes stripping the floor if needed and also sealing and buffing. The compounds used to seal concrete floor surfaces have no long lasting odour.
Images about Concrete Floor Tile Thickness
Concrete Floor Tile Thickness

Recent innovations in the capability to seal and stain concrete have raised its visual appeal, allowing it to participate with other stone flooring like marble, granite and slate – at a fraction of the cost. Be an intelligent person and embrace concrete as flooring surfaces that's not only safe for you but additionally to the planet.
Ceramic Tile – Thin-set vs Mud-set – Archtoolbox
The polished concrete is fast becoming a common issue in numerous places throughout the world and this is partly because a lot of men and women are appreciative of its beauty as well as since many places just are not able to stand having some other sort of floor. Sealed concrete has an incredibly low environmental impact.
How to Install Ceramic Tile Flooring in 9 Steps – This Old House
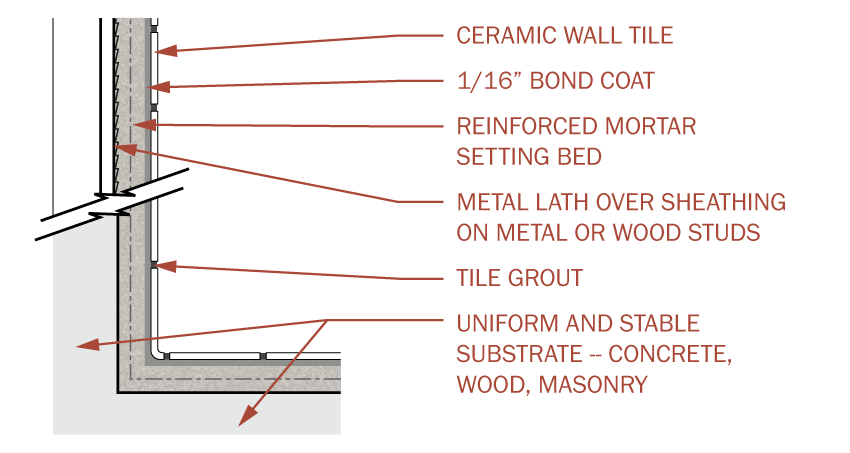
Floor Tile Installation Methods – Tile Doctor
Floor Tile Installation Methods – Tile Doctor
Floor Tile Installation Methods – Tile Doctor
Sound-Dampening Ceramic Tile over a Concrete Floor – Fine Homebuilding
Technical Focus: Critical Points of Ceramic Tile Design and
Floor tile thickness mm – Knowledge – Foshan Hanse Industrial Co.,Ltd
20mm Thickness Concrete Effect Tiles Marazzi
20mm Thickness Concrete Effect Tiles Marazzi
Subfloors and Underlayment for Ceramic Tile Floors
Tile Subfloor: Deflection, Thickness, Common Substrates
Mud floor thickness Ceramic tiles, Flooring, Mud
Related Posts:
- Patio Concrete Floor Coating
- How To Stain Concrete Floors Outdoors
- DIY Stained Concrete Floors In Homes
- Concrete Floors Look Like Marble
- Concrete Floor Slab Mix Ratio
- Dark Brown Concrete Floor Paint
- Pretty Concrete Floors
- Stained Concrete Floors For Homes
- Decorative Concrete Floor Ideas
- Pouring A Concrete Floor In A Garage
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19496947/color_gutters_illo_web_1.jpg)








/best-subfloors-to-use-for-laying-tile-1822586-hero-efcfac9422ab457da5d2cbc7f7361df7.jpg)

