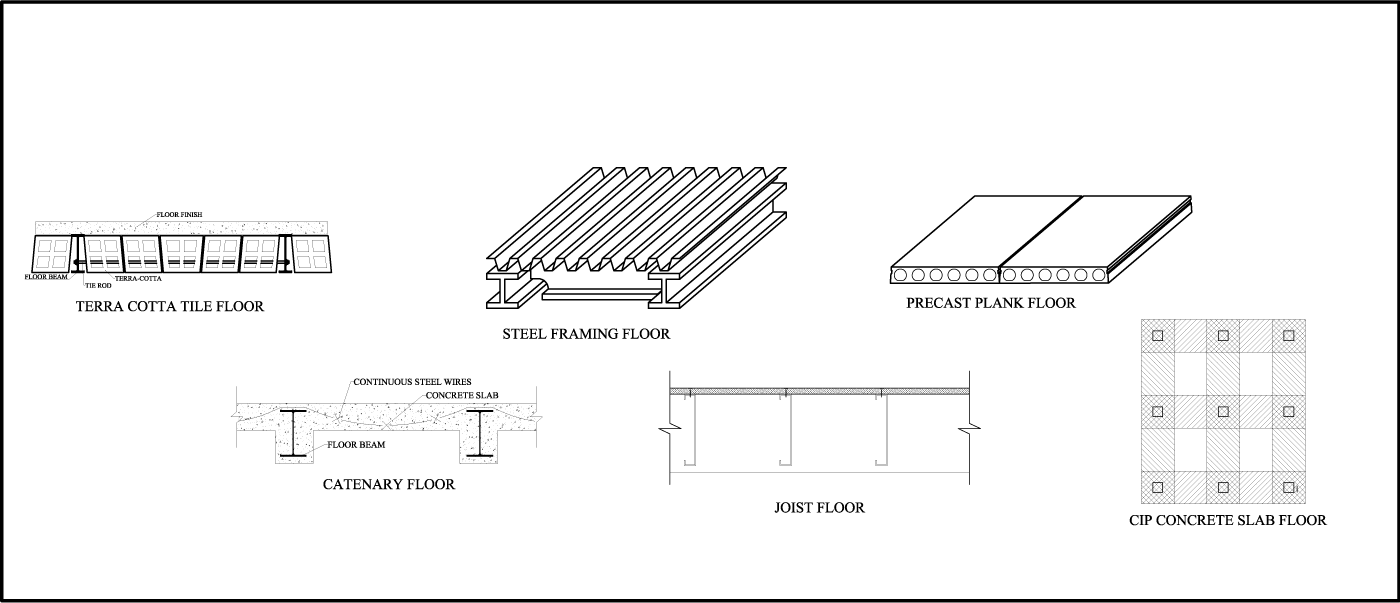
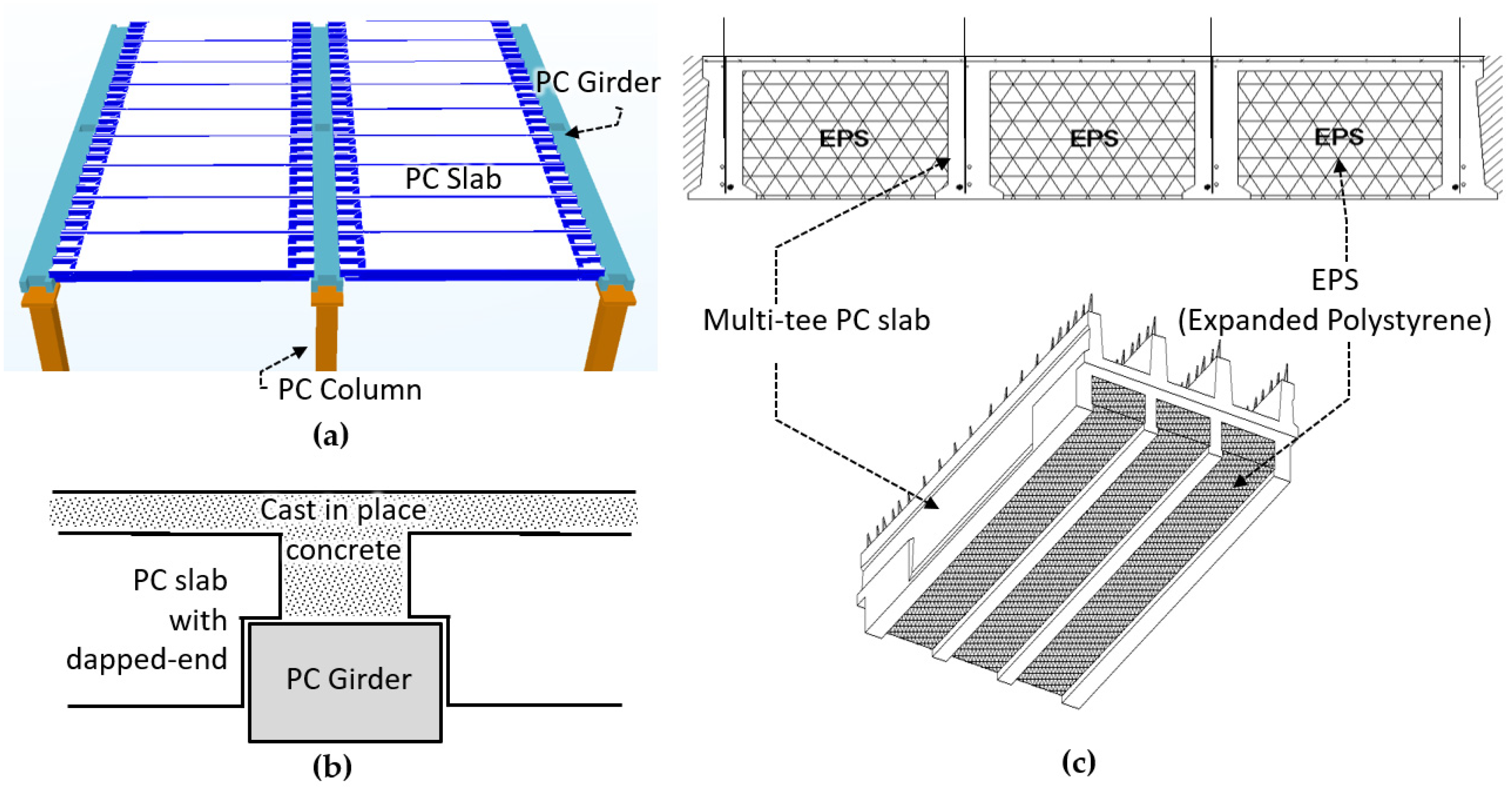
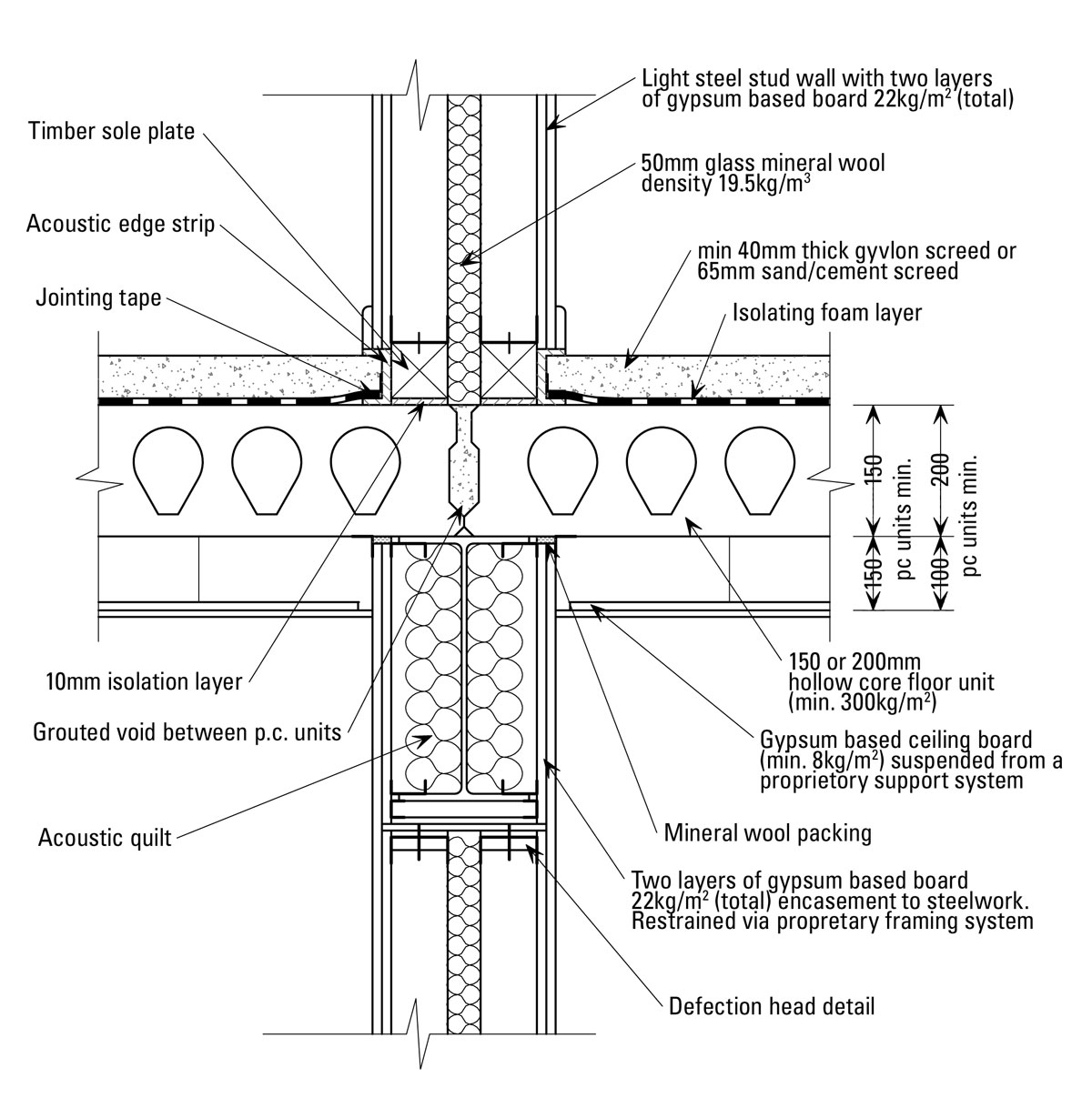
The Advantages of Precast Concrete Floor Construction
Precast concrete floor construction is becoming increasingly popular in the construction industry due to its numerous advantages. This article will explore the various benefits of using precast concrete for flooring purposes.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: One of the key advantages of precast concrete floor construction is its time and cost efficiency. Precast concrete floor elements are manufactured off-site, allowing for faster construction timelines. This method eliminates the need for on-site curing, resulting in reduced labor costs and quicker project completion.
- Superior Quality Control: Precast concrete floor elements are manufactured in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and strength. The use of standardized molds and manufacturing processes minimizes variations, resulting in highly reliable and durable flooring solutions. This quality control aspect reduces the risk of structural failures and enhances the overall longevity of the building.
- Versatility in Design: Precast concrete floor construction offers immense versatility in design. With a wide range of finishes, textures, and colors available, architects and designers have the freedom to create unique and aesthetically pleasing floor designs. Additionally, precast concrete floors can be customized to accommodate various architectural requirements, such as irregular shapes or curved layouts.
- Fire Resistance and Sound Insulation: Precast concrete floors provide excellent fire resistance, making them a preferred choice for buildings that require enhanced fire safety measures. The inherent properties of concrete, combined with additional fire-resistant materials, ensure that these floors can withstand high temperatures and protect the structural integrity of the building. Furthermore, precast concrete floors also offer superior sound insulation, minimizing noise transmission between different levels of a building.
- Environmental Sustainability: Precast concrete floor construction is environmentally sustainable due to several reasons. Firstly, the manufacturing process reduces waste generation and minimizes the use of natural resources. The durability of precast concrete floors also contributes to their sustainability, as they have a longer lifespan compared to traditional flooring materials. Additionally, the thermal mass properties of concrete contribute to energy efficiency by reducing heating and cooling requirements.

The Process of Precast Concrete Floor Construction
The process of precast concrete floor construction involves several stages, each contributing to the successful creation of durable and efficient flooring systems. We will provide an overview of the key steps involved in the process.
Design and Engineering: The first step in precast concrete floor construction is the design and engineering phase. Architects and structural engineers collaborate to develop the floor layout, considering factors such as load-bearing capacity, span lengths, and architectural requirements. Computer-aided design (CAD) software is often used to create detailed plans and specifications.
Manufacturing of Precast Concrete Elements: Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing of precast concrete elements begins. Reinforced concrete is poured into molds, which can be customized to achieve specific shapes and sizes. The concrete is left to cure and gain strength in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality.
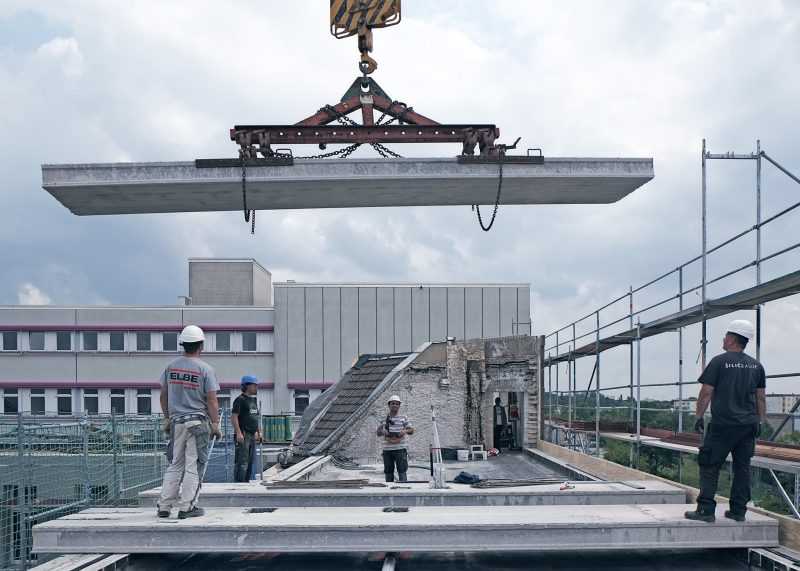
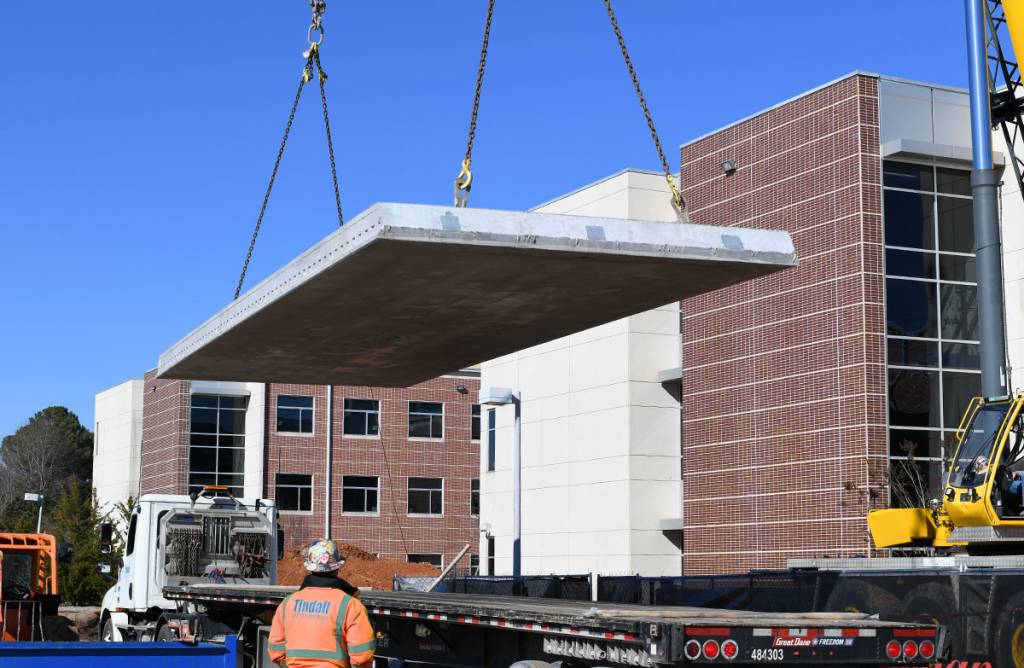
Transportation and Installation: After the precast concrete elements are manufactured, they are transported to the construction site. Cranes or other lifting equipment are used to carefully position and install the floor elements according to the design plans. Proper alignment and connection of the elements are crucial to ensure structural integrity.
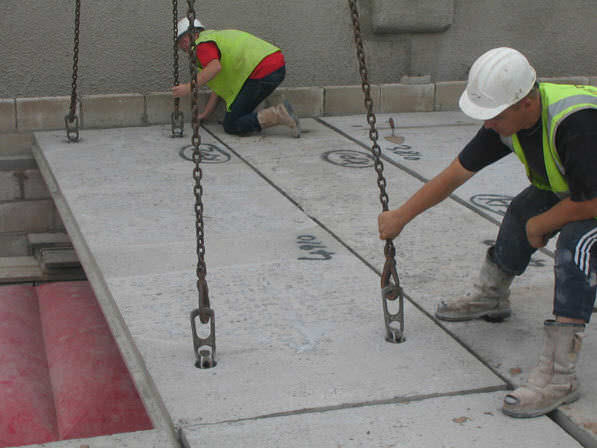
Jointing and Grouting: Once the precast concrete elements are in place, jointing and grouting are performed. Joints between the elements are filled with sealants or grout to ensure a watertight and secure connection. This step helps to prevent moisture penetration and enhances the overall stability of the floor system.
Finishing and Surface Treatments: After the joints are sealed, finishing and surface treatments are applied to the precast concrete floor. This can include polishing, staining, or applying protective coatings to enhance the aesthetics and durability of the flooring. Surface treatments also contribute to the ease of maintenance and cleaning.
Quality Assurance and Testing: Throughout the entire process of precast concrete floor construction, quality assurance and testing play a vital role. Regular inspections are conducted to ensure that the manufacturing, transportation, installation, and finishing processes meet the required standards. Testing for strength, durability, and other performance parameters is also carried out to verify the quality of the finished floor.
Design Considerations for Precast Concrete Floors
Designing precast concrete floors requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Let’s discuss key design considerations that architects and engineers should keep in mind when incorporating precast concrete floors into their projects.
Load-Bearing Capacity: The load-bearing capacity of precast concrete floors is a critical design consideration. The floor system must be able to support the weight of occupants, furniture, equipment, and any additional live loads. Structural engineers calculate the required strength and thickness of the precast elements to ensure safe and efficient load transfer.
Span Length and Deflection: The span length of precast concrete floors impacts their deflection and overall structural performance. Longer spans may require additional support, such as beams or columns, to minimize deflection and ensure the floor remains level. Engineers analyze the anticipated loads and select appropriate reinforcement to achieve the desired deflection limits.
Integration with Other Building Systems: Precast concrete floors need to integrate seamlessly with other building systems, such as electrical, plumbing, and HVAC. During the design phase, coordination among different disciplines is essential to ensure proper placement of openings, penetrations, and service routes. This coordination minimizes conflicts and facilitates efficient installation and maintenance of building systems.
Acoustic Considerations: Noise transmission between floors can be a concern in multi-story buildings. Designers must consider acoustic performance when incorporating precast concrete floors. Strategies such as adding sound-absorbing materials, using resilient mounts, or implementing floating floor systems can help reduce noise transmission and improve occupant comfort.
Fire and Thermal Performance: Precast concrete floors offer inherent fire resistance due to the properties of concrete. However, designers should consider additional fire protection measures, such as fire-rated coatings or the use of fire-resistant insulation materials, to meet specific building code requirements. Thermal performance is also a consideration, and designers may incorporate insulation layers or incorporate thermal breaks in the design to enhance energy efficiency.
Aesthetics and Architectural Intent: Precast concrete floors offer design flexibility, allowing architects to create visually appealing spaces. The selection of finishes, colors, and textures can significantly impact the overall aesthetics of the floor. Designers should consider the architectural intent and select precast elements that complement the building’s design concept.
Quality Control Measures in Precast Concrete Floor Construction
Maintaining high-quality standards is crucial in precast concrete floor construction to ensure the durability, safety, and performance of the finished product. Here are the key quality control measures that are implemented throughout the entire process of precast concrete floor construction.
Raw Material Selection and Testing: Quality control begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials for the production of precast concrete floor elements. Cement, aggregates, admixtures, and reinforcements must meet specified standards and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they possess the required strength and durability properties.
Precast Element Manufacturing: During the manufacturing process, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure consistent product quality. Regular testing of concrete mixtures, reinforcement placement, and curing conditions is carried out to verify compliance with design specifications. Non-destructive testing techniques, such as ultrasonic testing or visual inspections, may be employed to identify any defects or imperfections.
Molds and Formwork Inspection: The quality of molds and formwork used in precast concrete floor construction is crucial to achieving accurate and precise dimensions. Regular inspection and maintenance of molds and formwork are necessary to ensure they are in good condition and free from defects that could affect the final product’s quality.
Transportation and Installation: Quality control measures extend to the transportation and installation of precast concrete floor elements. Adequate protection and securing methods are employed during transportation to prevent damage. During installation, proper alignment, and connection of the elements are ensured to maintain the structural integrity of the floor system.
Jointing and Grouting Inspection: The jointing and grouting process is a critical stage in precast concrete floor construction. Quality control measures include inspecting the joints for proper alignment, ensuring the correct application of sealants or grout, and verifying the integrity of the joint seals. This inspection helps to prevent water infiltration and ensures a secure connection between the precast elements.
Final Inspection and Testing: Before the completion of precast concrete floor construction, a final inspection and testing phase is conducted. This comprehensive review involves checking the overall quality, dimensions, and finishes of the precast elements. Testing for structural performance, fire resistance, and sound insulation may also be carried out to validate compliance with design and regulatory requirements.
Sustainable Benefits of Precast Concrete Floor Construction
In today’s construction industry, sustainability is a key consideration. Precast concrete floor construction offers several sustainable benefits that make it an environmentally-friendly choice. We will explore the sustainable advantages of using precast concrete floors in construction projects.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Precast concrete floor construction helps reduce the carbon footprint of buildings. The manufacturing process of precast elements requires less energy compared to traditional on-site concrete construction. Additionally, precast concrete floors have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated carbon emissions from manufacturing new materials.
Waste Reduction: Precast concrete floor construction minimizes waste generation during the manufacturing process. Precise measurements and standardized molds result in minimal material wastage. Any excess concrete can be recycled or repurposed for other construction projects. This waste reduction contributes to a more sustainable and efficient construction process.
Energy Efficiency: Precast concrete floors offer excellent thermal mass properties, which can contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. The thermal mass of concrete helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and releasing heat slowly, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. This energy-saving characteristic can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions over the building’s lifespan.
Improved Indoor Air Quality: The use of precast concrete floors can enhance indoor air quality. Concrete materials do not emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful substances, contributing to a healthier indoor environment. Additionally, precast concrete floors can be designed with proper insulation to minimize the potential for moisture infiltration and mold growth, further improving indoor air quality.
Recyclability and Reusability: Precast concrete floor elements are highly recyclable and reusable. At the end of a building’s life cycle, precast elements can be dismantled and repurposed for new construction projects. The recyclability and reusability of precast concrete floors reduce the demand for new materials and minimize waste generation, contributing to a more sustainable construction industry.
Stormwater Management: Precast concrete floors can be designed with integrated stormwater management systems. By incorporating features such as permeable surfaces or channels for water collection and filtration, precast concrete floors can help manage stormwater runoff effectively. This reduces the strain on municipal drainage systems and promotes sustainable water management practices.
Opportunities for precast prestressed concrete floor slabs in
PreCast Construction Precast concrete, Precast concrete slabs
AD 313: Precast concrete floors in steel framed buildings
T-SLAB takes precast concrete floor systems to the next level
Precast concrete formwork, floor system and a method of
Toppings and Screeds for Precast Concrete Floors – Fibre Concrete
Reinforced concrete precast core floor slab – Thomas Armstrong
Situ Concrete – an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Related Posts:
- Acid Wash Concrete Floor Colors
- Concrete Floor Thickness For A Garage
- Concrete Floor For Bathroom
- Interior Concrete Floor Ideas
- Kitchen Stained Concrete Floors
- Concrete Floor Tile Thickness
- How To Stain Concrete Floors DIY
- DIY Concrete Floor Grinding
- Concrete Floor Damage
- Faux Stained Concrete Floors