Introduction to Precast Concrete Floor Construction
Precast concrete floor construction is a method widely used in the construction industry to create durable and efficient flooring systems. This technique involves the manufacturing of precast concrete elements off-site, which are then transported and assembled on-site to form a complete floor structure.
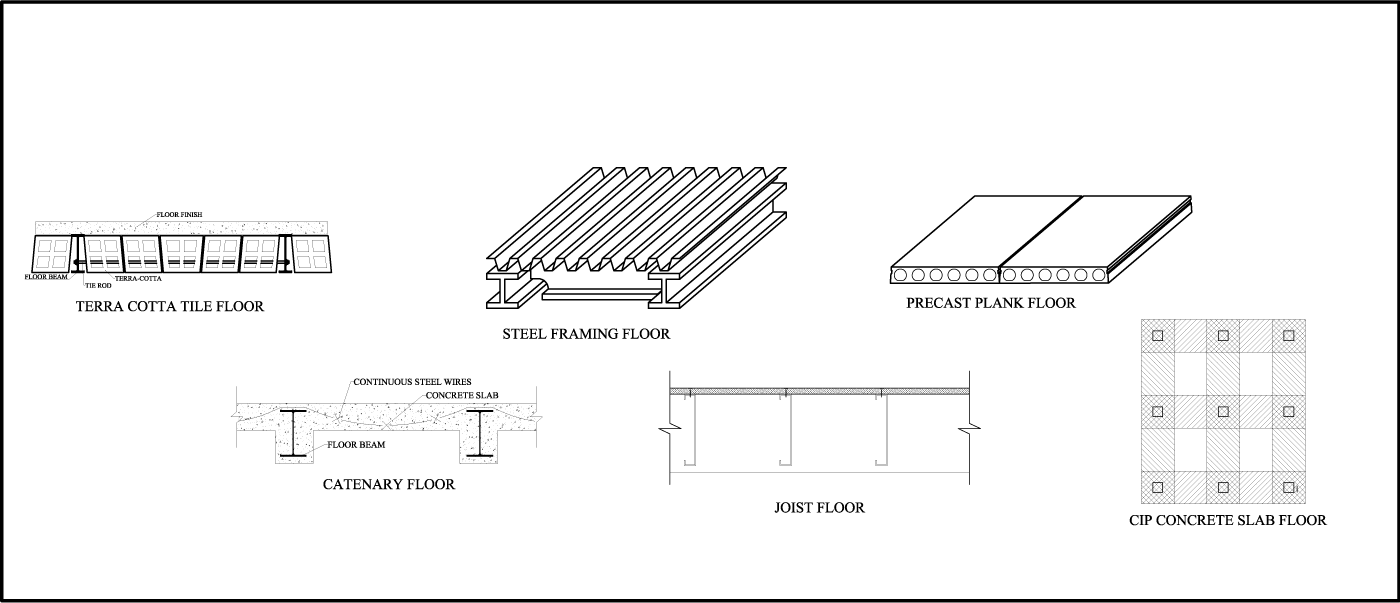
The process of precast concrete floor construction begins with the design and fabrication of the precast elements. These elements are typically large panels or planks that are cast in a controlled environment, such as a factory or precast yard. They are manufactured using high-quality concrete and reinforcing materials to ensure strength and durability.
Once the precast elements are ready, they are transported to the construction site and installed using cranes or other lifting equipment. The elements are usually connected together through various methods, such as welding, bolting, or grouting, to create a solid and stable floor structure.
One of the key advantages of precast concrete floor construction is its speed and efficiency. Since the precast elements are manufactured off-site, construction activities can proceed simultaneously at the site. This can help reduce construction time and overall project duration. Additionally, the quality of precast elements can be closely monitored and controlled, resulting in consistent and reliable flooring systems.
Precast concrete floor construction also offers flexibility in design and customization. The precast elements can be manufactured in various shapes, sizes, and finishes to meet specific project requirements. This allows architects and designers to create unique and aesthetically pleasing flooring solutions.
Moreover, precast concrete floor construction offers several benefits in terms of sustainability and environmental impact. The use of precast elements reduces the amount of formwork and scaffolding required, minimizing waste generation. Additionally, the durability and longevity of precast concrete floors contribute to the overall lifespan of the building, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
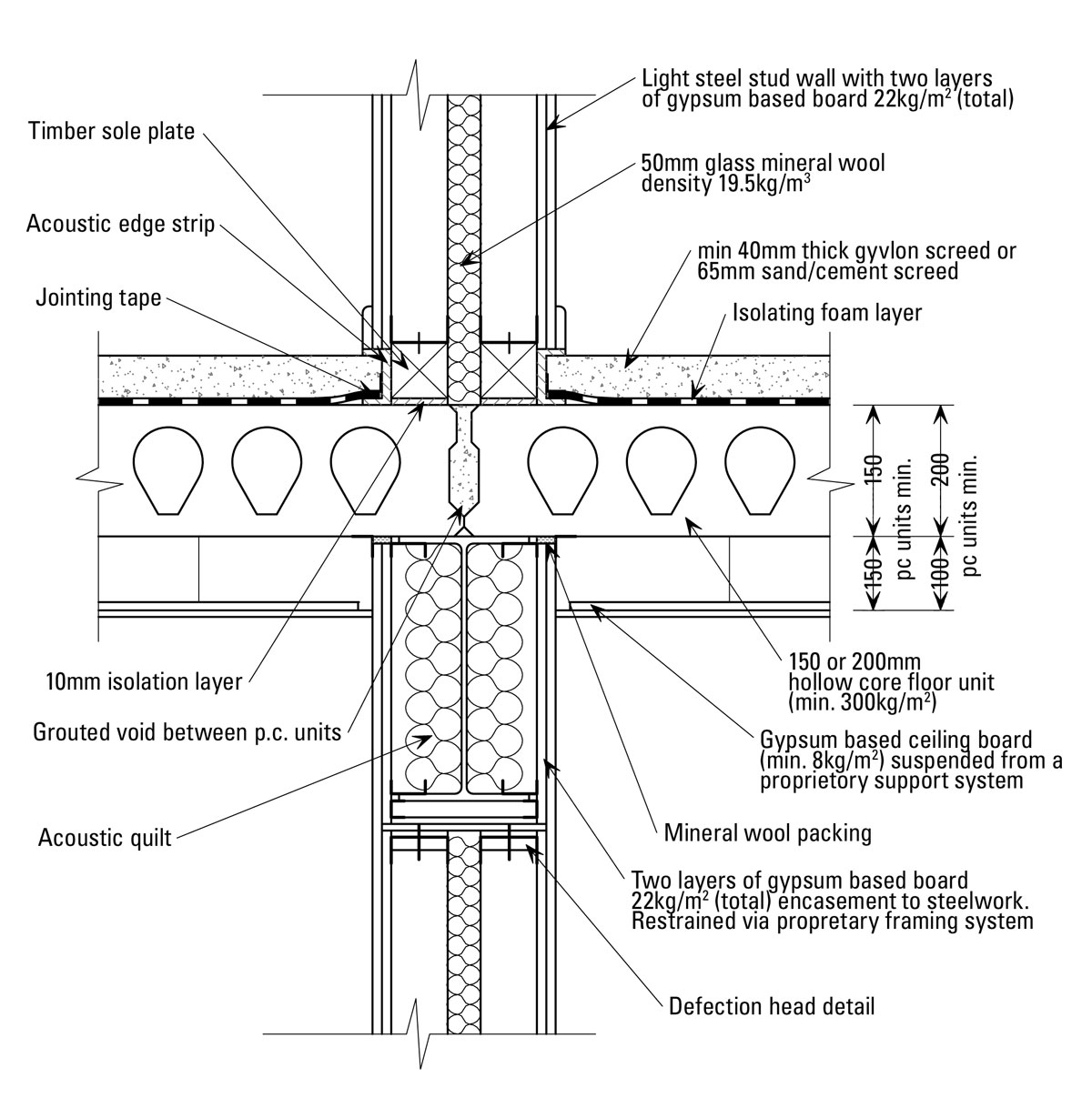
Key Components for Precast Concrete Floor Construction
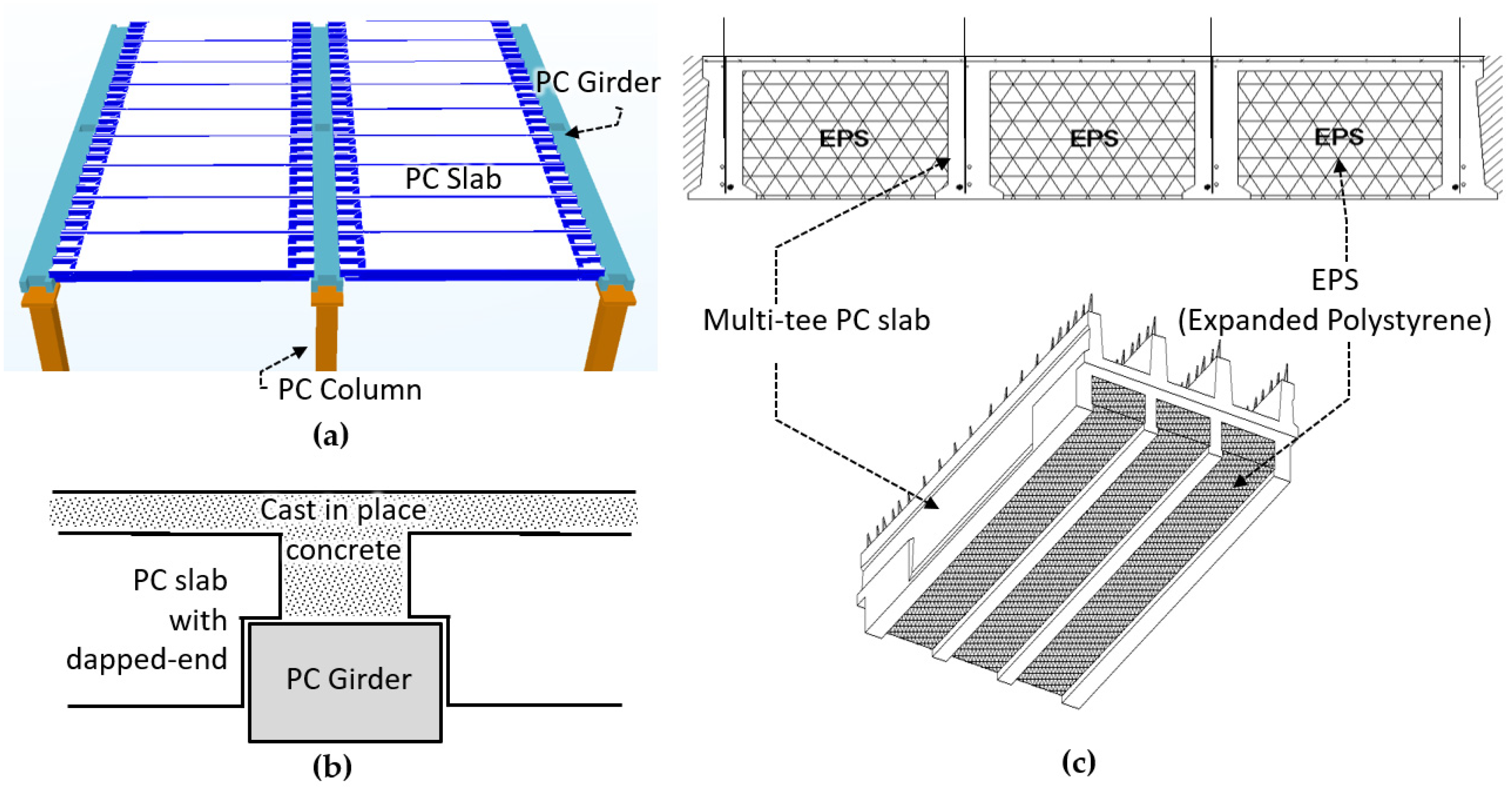
Precast Concrete Slabs: The main component of precast concrete floor construction is the precast concrete slabs. These slabs are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment and then transported to the construction site for installation. They are designed to provide the necessary strength and durability to support the loads imposed on the floor.
Reinforcement: Reinforcement is an essential component of precast concrete floor construction. Steel reinforcement, such as rebar or wire mesh, is embedded within the precast concrete slabs to enhance their structural integrity and resistance to cracking. The placement and orientation of the reinforcement are carefully planned to ensure optimal performance of the floor.
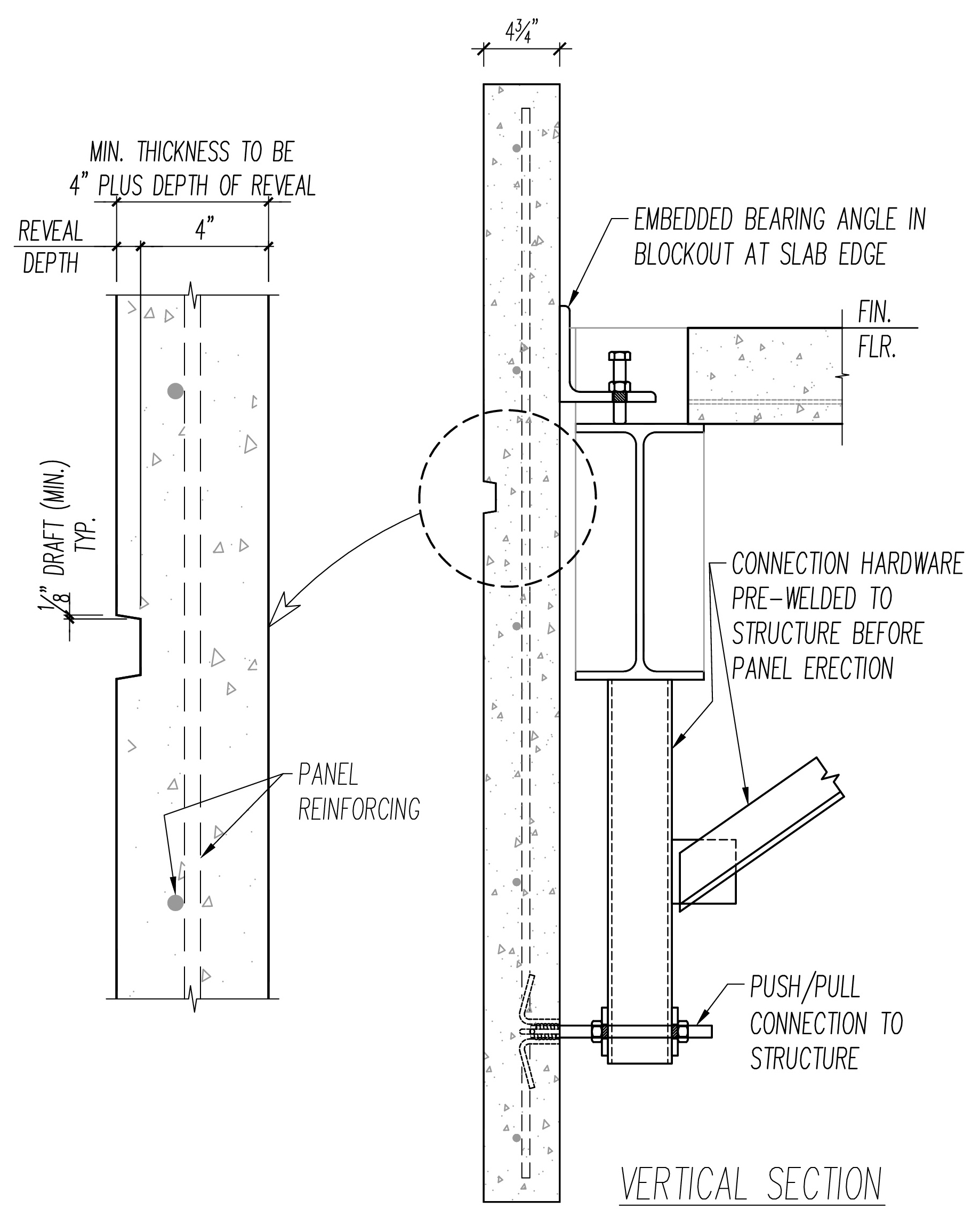
Connections: Precast concrete slabs need to be securely connected to each other and to the supporting structure. Various types of connections, such as dowels, shear keys, and connectors, are used to achieve this. These connections not only ensure the stability of the floor system but also facilitate the transfer of loads between adjacent slabs and the supporting structure.
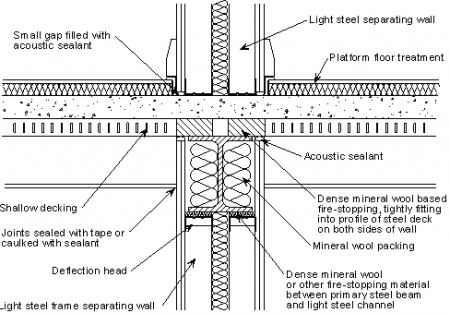
Jointing: Joints are a critical aspect of precast concrete floor construction. They allow for movement and accommodate the expansion and contraction of the concrete due to temperature changes. Proper joint design and installation are crucial to prevent cracking and maintain the overall performance of the floor system.
Design Considerations for Precast Concrete Floor Construction
Load Requirements: The design of precast concrete floor systems should consider the specific loads that the floor will experience. This includes dead loads, such as the weight of the floor itself, as well as live loads, such as occupants and furnishings. The structural design should ensure that the precast concrete slabs can safely support these loads without excessive deflection or failure.
Span Lengths: The span lengths between supports play a significant role in the design of precast concrete floor systems. Longer spans require thicker and stronger precast concrete slabs to resist bending and deflection. The design should strike a balance between achieving longer spans for increased flexibility and minimizing the size and weight of the slabs for cost-effective construction.
Fire Resistance: Precast concrete floor systems should be designed to provide adequate fire resistance. This may involve incorporating fire-resistant materials or coatings, or designing the system to ensure that it can withstand fire for a specified duration without compromising its structural integrity.
Installation and Construction Process for Precast Concrete Floor Systems
When it comes to the installation and construction process of precast concrete floor systems, several important steps need to be followed to ensure a successful and efficient outcome. Below are the key details to consider during this process:
- Site Preparation: The first step in the installation process is to prepare the site where the precast concrete floor system will be installed. This involves clearing the area, leveling the ground, and ensuring a stable foundation for the floor system.
- Delivery and Placement: Once the site is prepared, the precast concrete floor system components are delivered to the construction site. These components, which are manufactured off-site, are then carefully lifted and placed into position using cranes or other appropriate equipment.
- Connection and Alignment: After the precast concrete floor system components are placed, they need to be properly connected and aligned. This requires ensuring that the joints between the components are properly sealed and that they fit together securely. The alignment of the components is also crucial to ensure a level and structurally sound floor system.
- Grouting and Finishing: Once the precast concrete floor system components are connected and aligned, the next step is to grout the joints between the components. Grouting helps to provide additional strength and stability to the floor system. After grouting, any necessary finishing touches, such as applying a sealer or a protective coating, can be done to enhance the durability and aesthetics of the floor system.
- Post-Installation Checks: Once the precast concrete floor system is installed, it is important to conduct post-installation checks to ensure its quality and performance. These checks may include inspections for any defects or imperfections, as well as load testing to verify the load-bearing capacity of the floor system.
Benefits and Advantages of Using Precast Concrete Floor Construction
Speed of construction: Precast concrete floor construction offers significant time savings compared to traditional cast-in-place methods. The precast elements are manufactured off-site in controlled environments, allowing for concurrent site preparation and construction. This results in faster project completion and reduced construction time.
Quality control: Precast concrete floor construction ensures high-quality and consistent products. The manufacturing process involves strict quality control measures, resulting in uniformity and precision. The controlled environment eliminates the risk of weather-related issues and ensures the production of durable and reliable components.
Cost-effective: Although the initial costs of precast concrete floor construction may be higher than traditional methods, the long-term benefits outweigh the investment. The speed of construction reduces labor costs and allows for earlier occupancy, generating revenue or cost savings sooner. Additionally, the high-quality precast elements require minimal maintenance, reducing long-term expenses.
Flexibility and versatility: Precast concrete floor construction offers a wide range of design options due to the flexibility and versatility of precast elements. Architects and engineers have the freedom to create unique and complex designs, including curved or irregular shapes, without compromising on structural integrity. The precast elements can also be easily modified or expanded, allowing for future adaptability.
Durability and sustainability: Precast concrete floor construction is known for its durability and long lifespan. The high-strength concrete and reinforcement used in precast elements provide excellent resistance to weathering, corrosion, and fire. The durability of precast concrete also minimizes the need for repairs or replacements, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Improved safety: The use of precast concrete floor construction enhances safety on construction sites. The off-site manufacturing process reduces the need for extensive on-site work, minimizing potential hazards and risks to workers. Additionally, precast elements can be easily transported and installed, reducing the need for heavy machinery and improving overall site safety.
Noise and vibration reduction: Precast concrete floor construction offers excellent acoustic and vibration insulation properties. The dense and solid precast elements effectively reduce noise transmission, creating quieter indoor environments. This is particularly beneficial in residential or commercial buildings where noise reduction is essential for occupant comfort.
Energy efficiency: Precast concrete floor construction contributes to improved energy efficiency in buildings. The thermal mass properties of precast concrete help regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This leads to lower energy consumption, decreased environmental impact, and potential cost overhead.
Precast Concrete – an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Best 25 Precast Concrete Slabs Ideas On Plunge Pool Precast
Precast concrete floor unit bearing an reinforced concrete beam
Situ Concrete – an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Architectural Precast Manufacturing Process by Willis Construction
a). Construction drawings for walls and floor of precast concrete
STRUCTURE magazine Creating an Opening in Existing Floors
Applied Sciences Free Full-Text Development of Multi-Tee-Type
PreCast Construction Precast concrete, Precast concrete slabs
3 Detailed section for precast concrete alternative (CC
Related Posts:
- Polished Concrete Floors For Patios
- White Concrete Floor Tiles
- Acid Wash Concrete Floor Colors
- Concrete Floor Thickness For A Garage
- Concrete Floor For Bathroom
- Interior Concrete Floor Ideas
- Kitchen Stained Concrete Floors
- Concrete Floor Tile Thickness
- How To Stain Concrete Floors DIY
- DIY Concrete Floor Grinding