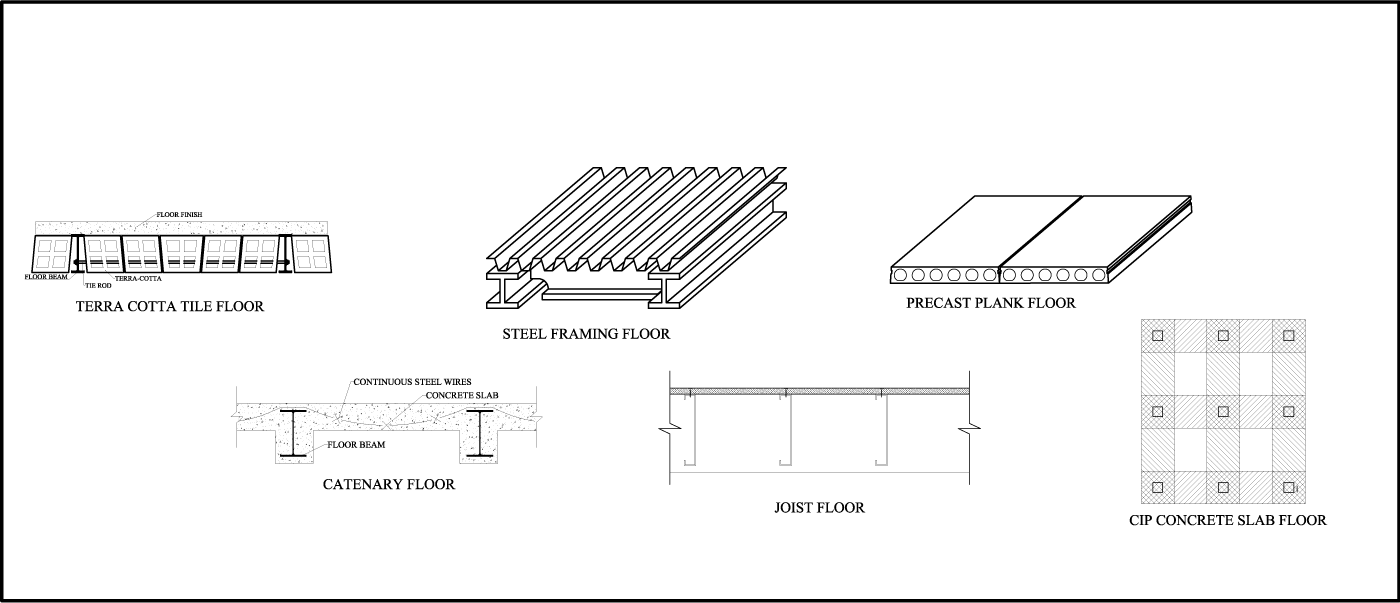
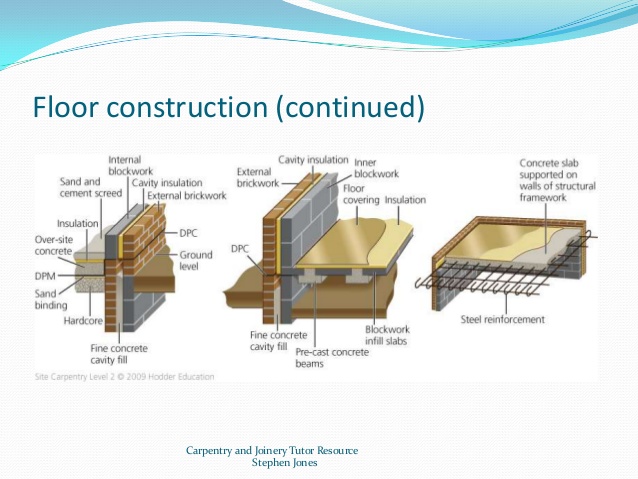
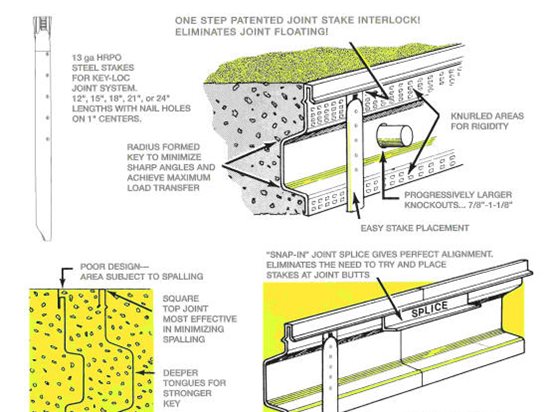
Importance of Proper Construction Techniques for Concrete Floor Slabs
When it comes to building structures, the foundation is crucial. The same principle applies to concrete floor slabs. Proper construction techniques play a vital role in ensuring the durability and longevity of these slabs. Let’s discuss the importance of using the right techniques during the construction of concrete floor slabs.
- Ensuring Structural Integrity: One of the primary reasons for using proper construction techniques is to ensure the structural integrity of the concrete floor slab. This involves proper site preparation, adequate reinforcement, and accurate pouring and leveling of the concrete. By following these techniques, we can prevent cracks, settling, and other structural issues that can compromise the stability and safety of the floor slab.
- Enhancing Load-Bearing Capacity: Concrete floor slabs are designed to bear heavy loads. By using proper construction techniques, we can enhance the load-bearing capacity of the slab. This includes considering factors such as the thickness of the slab, reinforcement placement, and joint design. The use of appropriate techniques will ensure that the floor slab can withstand the intended load without experiencing excessive deflection or failure.
- Minimizing Future Maintenance Costs: Investing in proper construction techniques upfront can help minimize future maintenance costs associated with concrete floor slabs. By using techniques such as proper curing, sealing, and finishing, we can reduce the likelihood of surface defects, staining, and deterioration. This will save both time and money in the long run, as the floor slab will require less frequent repairs and maintenance.
- Improving Aesthetics and Functionality: Concrete floor slabs are not only functional but can also enhance the aesthetics of a space. Proper construction techniques, such as using high-quality materials, precise leveling, and decorative finishes, can greatly improve the appearance of the floor slab. Additionally, techniques like proper joint placement and surface treatments can enhance the functionality of the floor, allowing for easier cleaning and increased slip resistance.
- Ensuring Compliance with Building Codes and Regulations: Proper construction techniques are essential to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations. These codes often outline specific requirements for concrete floor slabs, including thickness, reinforcement, and finishing. By following the recommended techniques, builders can avoid penalties, delays, and potential legal issues associated with non-compliance.
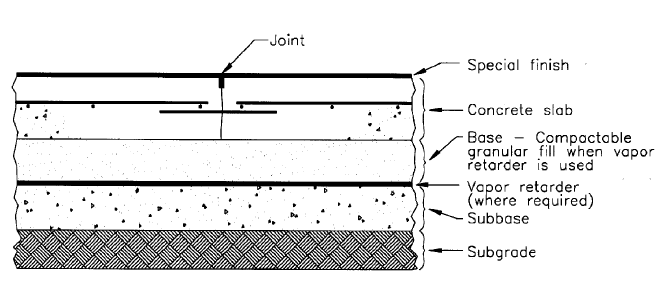
Key Steps in Constructing a Concrete Floor Slab
Constructing a concrete floor slab requires careful planning and execution to ensure a strong and stable foundation. We will outline the key steps involved in the construction process, providing a comprehensive guide for builders and contractors.
Site Preparation: Before pouring concrete for the floor slab, proper site preparation is essential. This includes clearing the area of any debris or vegetation, leveling the ground, and compacting the soil to provide a stable base. It is crucial to ensure that the site is properly graded to prevent water pooling and to allow for proper drainage.
Formwork Installation: Formwork serves as a mold for the concrete and provides shape and support during the pouring and curing process. The formwork should be constructed using high-quality materials and properly aligned to ensure a level and even floor surface. Careful attention should be given to the placement of form ties and bracing to prevent any movement during the pouring process.
Reinforcement Placement: Reinforcement, such as steel bars or mesh, is crucial for enhancing the strength and durability of the concrete floor slab. The reinforcement should be properly positioned within the formwork, ensuring adequate coverage and spacing as specified by structural engineers. This will help distribute loads evenly and minimize the risk of cracking or structural failure.
Concrete Pouring: Once the formwork and reinforcement are in place, the next step is to pour the concrete. The concrete mix should be carefully prepared, considering factors such as the desired strength, workability, and curing time. During pouring, it is important to maintain a consistent flow of concrete and avoid segregation or voids. Proper consolidation techniques, such as vibration, should be employed to eliminate air pockets and ensure a dense and uniform concrete mix.
Leveling and Finishing: After the concrete is poured, it needs to be leveled and finished to achieve a smooth and even surface. This involves using tools like screeds and floats to remove excess concrete and create a leveled finish. To enhance the durability and aesthetics of the floor slab, additional finishing techniques like troweling, stamping, or polishing can be applied.
Curing and Protection: Curing is a crucial step in the construction process as it allows the concrete to gain strength and achieve its desired properties. Proper curing involves maintaining a moist environment and controlling the temperature to promote hydration and prevent cracking. Curing compounds or moisture-retaining coverings can be used to facilitate the curing process. It is also important to protect the newly poured concrete from excessive traffic or loads until it has fully cured.
Common Challenges in Concrete Floor Slab Construction and How to Overcome Them
The construction of concrete floor slabs can present various challenges that builders and contractors need to be aware of. Let’s discuss some of the common challenges faced during the construction process and provide strategies to overcome them effectively.
Uneven Subgrade: One common challenge is dealing with an uneven subgrade, which can affect the stability and levelness of the floor slab. To overcome this, proper site preparation is essential. Compacting the subgrade and using leveling materials, such as granular fill or sand, can help create a more even surface. Additionally, using laser-guided grading techniques can ensure precise leveling.
Control of Cracking: Cracking is a common concern in concrete floor slabs due to factors like shrinkage, temperature changes, or inadequate reinforcement. To overcome this challenge, builders can use techniques such as proper joint placement to control crack locations. Incorporating reinforcement, such as steel fibers or rebar, can also help minimize crack widths and improve overall durability.
Moisture-related Issues: Moisture-related problems, such as excessive moisture vapor transmission or moisture intrusion, can impact the performance and longevity of concrete floor slabs. To overcome these challenges, builders can use moisture barriers or vapor retarders during the construction process. It is also important to ensure proper drainage and implement moisture mitigation strategies, such as applying moisture-resistant coatings or sealants.
Surface Defects and Finishing Issues: Achieving a smooth and aesthetically pleasing finish can be a challenge in concrete floor slab construction. Surface defects like spalling, scaling, or uneven finish can occur due to improper finishing techniques or inadequate curing. Overcoming these challenges requires attention to detail during finishing, including proper troweling, timing of finishing operations, and implementing appropriate curing methods.
Adequate Load-bearing Capacity: Ensuring that a concrete floor slab can adequately bear the intended loads is crucial. Challenges related to load-bearing capacity can arise from inadequate thickness, improper reinforcement, or poor construction practices. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to follow structural engineering recommendations for slab thickness and reinforcement placement. Employing load testing methods can also help ensure the floor slab’s capacity meets the required standards.
Choosing the Right Materials for a Durable and Long-lasting Concrete Floor Slab
Selecting the right materials is crucial for constructing a durable and long-lasting concrete floor slab. We will discuss the key considerations for choosing materials and provide insights into the best options available in the market.
Concrete Mix: The foundation of a concrete floor slab is the concrete mix itself. It is important to choose a high-quality mix that meets the specific requirements of the project. Factors to consider include the desired strength, workability, and durability. Utilizing a well-graded aggregate, appropriate cementitious materials, and admixtures designed for specific purposes can enhance the performance and longevity of the concrete floor slab.
Reinforcement: Reinforcement materials, such as steel bars or mesh, play a vital role in enhancing the strength and durability of the concrete floor slab. The selection of reinforcement depends on the anticipated loads and requirements specified by structural engineers. Common options include steel rebar, welded wire fabric, or steel fibers. Choosing the right reinforcement type, size, and placement is essential to ensure the structural integrity of the floor slab.
Vapor Retarders and Moisture Barriers: Moisture-related issues can significantly impact the performance of concrete floor slabs. To mitigate these issues, vapor retarders or moisture barriers are often used. These materials help prevent moisture intrusion from the subgrade or vapor transmission from the underlying soil. Common options include polyethylene sheets, epoxy coatings, or specialized moisture-blocking membranes. The choice of vapor retarder or moisture barrier depends on factors such as the project’s location, environmental conditions, and specific moisture concerns.
Finishing Materials: Choosing the right finishing materials is crucial for achieving the desired aesthetics and functionality. Surface treatments and coatings can enhance the appearance and durability of the concrete floor slab. Options include epoxy coatings, polyurethane sealers, or decorative toppings. Selecting materials that are compatible with the concrete mix and suitable for the intended use of the floor slab will ensure long-term performance and minimize maintenance requirements.
Best Practices for Maintaining and Repairing Concrete Floor Slabs
Proper maintenance and timely repairs are essential for preserving the integrity and functionality of concrete floor slabs. Here are several practices for maintaining and repairing concrete floor slabs, ensuring their longevity and minimizing the need for extensive repairs.
Regular Cleaning: Regular cleaning is crucial for maintaining the appearance and performance of concrete floor slabs. Sweep or vacuum the surface regularly to remove dirt, debris, and abrasive particles that can cause surface wear. Use a pH-neutral cleaner and a soft mop or scrub brush to remove stains or spills. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaning tools that can damage the surface.
Preventive Maintenance: Implementing preventive maintenance measures can significantly extend the lifespan of concrete floor slabs. Apply a quality sealer or coating to protect the surface from stains, moisture intrusion, and chemical damage. Ensure proper drainage to prevent water pooling or seepage. Regularly inspect the slab for cracks, spalling, or other signs of damage, and address them promptly to prevent further deterioration.
Repairing Cracks: Cracks can occur in concrete floor slabs due to shrinkage, settlement, or heavy loads. Timely crack repair is crucial to prevent further damage and potential safety hazards. Small cracks can be repaired using epoxy or polyurethane-based crack fillers. For larger cracks or structural issues, consult a professional engineer to assess the severity and recommend appropriate repair methods, such as epoxy injection or full-depth repairs.
Surface Resurfacing: Over time, concrete floor slabs may develop surface wear, pitting, or unevenness. Surface resurfacing can restore the appearance and functionality of the slab. Options include applying a thin overlay, such as microtopping or self-leveling concrete, or using a decorative concrete topping. Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and profiling, is essential for a successful resurfacing application.
Joint Maintenance: Concrete floor slabs often have expansion joints or control joints to accommodate movement and prevent cracking. Regular inspection and maintenance of these joints are important. Remove any debris or sealant residue from the joints and replace damaged or deteriorated joint fillers. Properly maintaining the joints will help prevent moisture intrusion, reduce the risk of tripping hazards, and prolong the lifespan of the floor slab.
Slab On Grade Foundation Design Slab On Grade Design
Construction detail of the concrete slab-on-ground floored case
Floors – Types of floors – Methods of Construction of Floor
Concrete slab – Wikipedia
Construction Joints in Concrete Slabs – Concrete Network
combining radiant flour in slab on grade Concrete floors, Slab
Building Guidelines Concrete Floors, Slabs
Related Posts:
- How To Stain Concrete Floors Outdoors
- DIY Stained Concrete Floors In Homes
- Concrete Floors Look Like Marble
- Concrete Floor Slab Mix Ratio
- Dark Brown Concrete Floor Paint
- Pretty Concrete Floors
- Stained Concrete Floors For Homes
- Decorative Concrete Floor Ideas
- Pouring A Concrete Floor In A Garage
- How To Get Smooth Concrete Floor