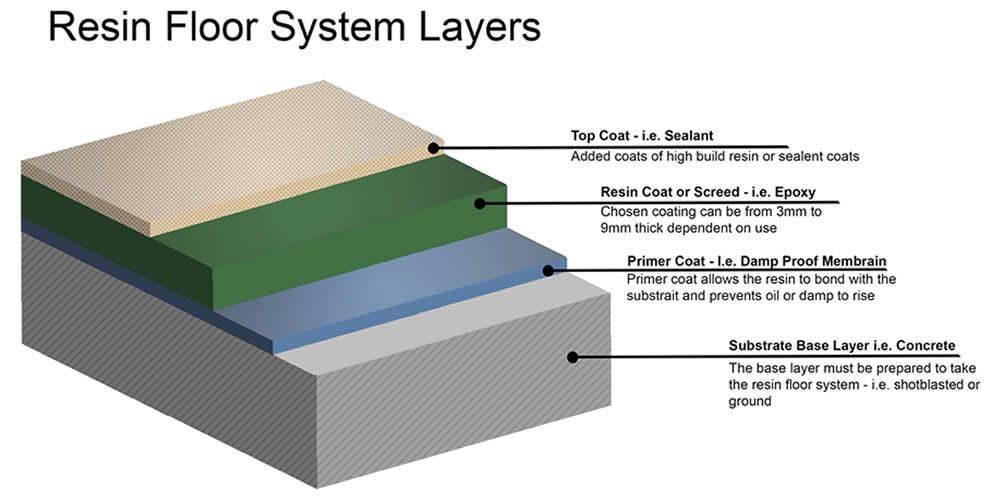
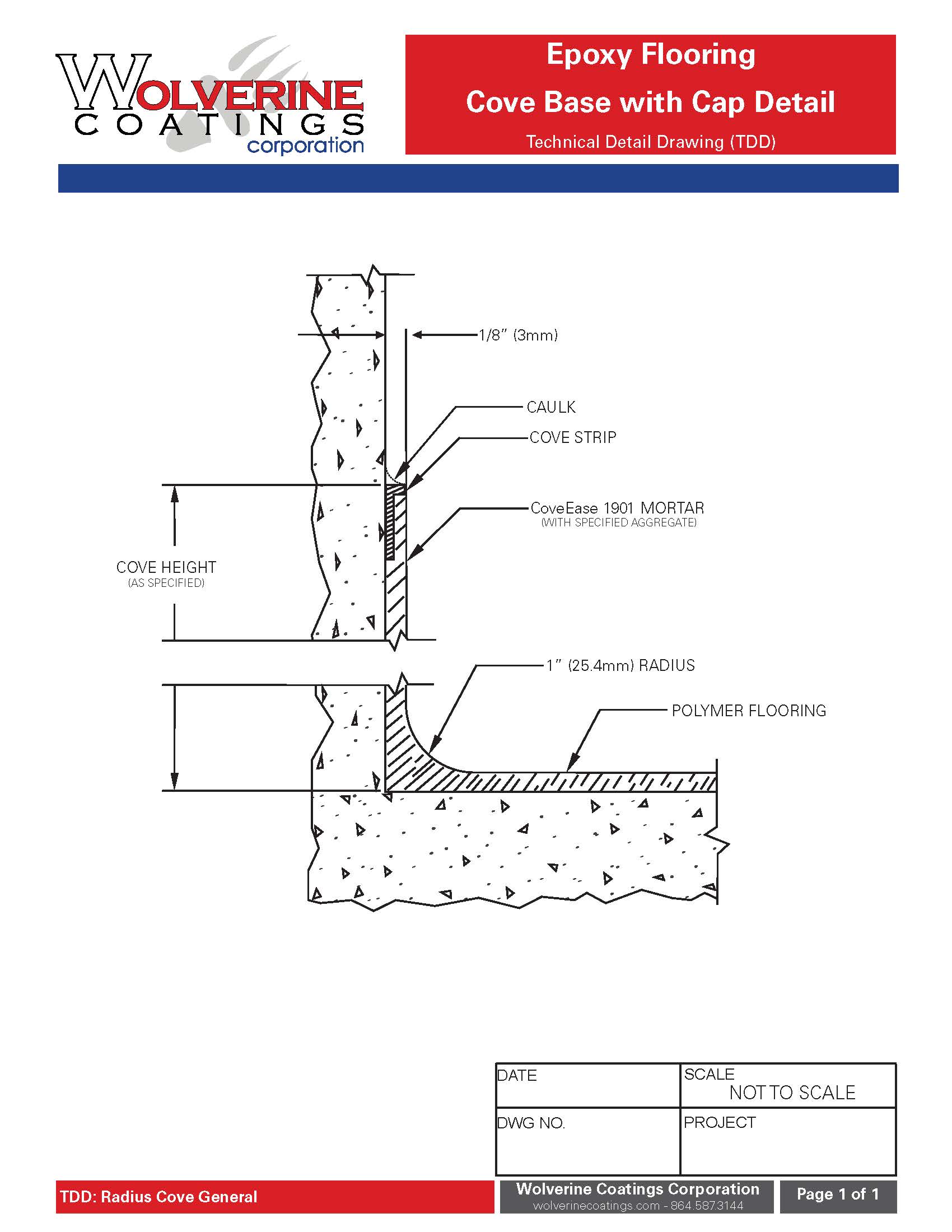
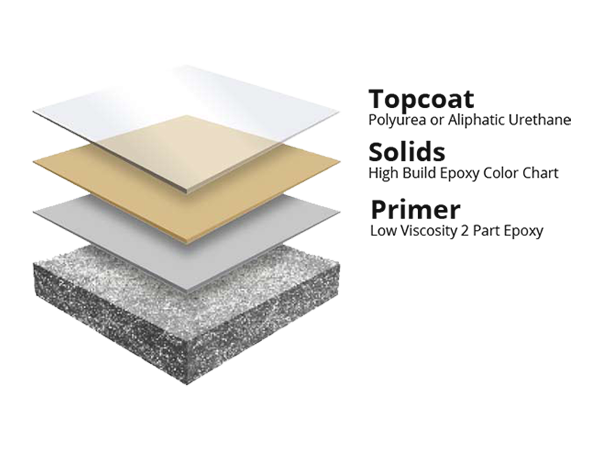
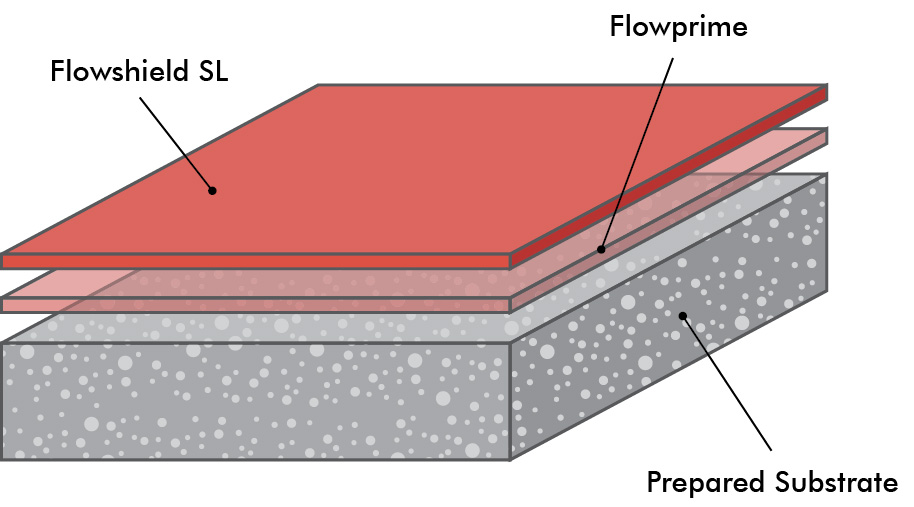
Epoxy floors have emerged as a top choice for their resilience, versatility, and stunning visual appeal. In this comprehensive guide, I want to delve into the technical aspects of epoxy flooring, providing a deeper understanding of the science behind this remarkable surface. By uncovering the chemistry, application techniques, and maintenance considerations, we can make informed decisions about choosing epoxy floors for our spaces and ensuring their long-lasting beauty and performance.
Understanding Epoxy Flooring
Epoxy flooring is more than just a coating; it is a carefully formulated combination of epoxy resin and hardeners, resulting in a chemically bonded, dense, and durable surface. The epoxy resin, a thermosetting polymer, provides exceptional adhesion to various substrates, while the hardeners initiate the crosslinking process that transforms the liquid epoxy into a solid, high-performance surface. This curing process creates a seamless, non-porous finish, making epoxy floors highly resistant to water, chemicals, and other common contaminants.
Epoxy Flooring Systems
Epoxy flooring comes in two main systems: solvent-based and water-based.
Solvent-based epoxy systems: These systems contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as a carrier solvent, which aids in the application and evaporation process. Solvent-based epoxy provides a durable, high-gloss finish and is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings due to its excellent chemical and abrasion resistance.
Water-based epoxy systems: In contrast, water-based epoxy is an environmentally friendly option, containing fewer VOCs and emitting minimal odors during application. Although it might lack the same glossy finish as solvent-based epoxy, water-based systems offer good adhesion and durability, making them suitable for various environments, including residential spaces.
Surface Preparation for Epoxy Flooring
Surface preparation is a critical step in ensuring the success of an epoxy flooring installation. A properly prepared surface enhances adhesion and prevents issues like delamination and peeling.
Mechanical methods for surface profiling and cleaning: Shot blasting, grinding, and diamond tooling are common mechanical methods used to profile the surface, removing contaminants and creating a roughened texture that facilitates epoxy bonding.
Chemical treatments and etching for optimal adhesion: In cases where mechanical methods are not feasible, chemical treatments, such as acid etching, can be employed to prepare the substrate and promote epoxy adhesion.
Mixing and Application of Epoxy Flooring
Proper mixing and application techniques are vital to achieving a flawless and long-lasting epoxy floor.
Proper mixing of epoxy resin and hardener: I’ve learned that precise measurements and thorough mixing of epoxy resin and hardener are crucial to achieving a consistent and uniform blend.
Understanding pot life and workable time: Epoxy has a limited pot life, which refers to the time available for application before the mixture begins to cure. Understanding the pot life ensures that I have enough time to work with the epoxy without wasting any material.
Techniques for applying epoxy coatings on different surfaces: Epoxy can be applied using various methods such as roller application, brush application, or spray application. I select the appropriate technique based on the type of epoxy, the surface area, and the desired finish.
Epoxy Flooring Thickness and Build
The thickness of the epoxy floor is essential for its durability and performance.
Understanding epoxy floor thickness requirements: Different environments and usage demands may require specific epoxy thickness to withstand the intended level of traffic and stress.
Factors influencing the build and number of coats: The desired thickness and build of the epoxy floor depend on the substrate condition, epoxy type, and the specific requirements of the space.
Achieving a smooth and level surface with multiple coats: Applying multiple coats of epoxy ensures a uniform build and a smooth surface, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Epoxy Flooring Curing Process
The curing process is a crucial stage that determines the epoxy floor’s final properties and performance.
Stages of epoxy curing: The curing process occurs in several stages, including gel time (when the epoxy begins to thicken), cure time (when the epoxy becomes solid), and full cure (when the epoxy reaches its maximum strength).
Factors affecting the curing process and curing agents: Temperature, humidity, and the choice of curing agents can significantly influence the curing time and final characteristics of the epoxy floor.
Importance of curing conditions for long-term performance: Proper curing conditions, such as maintaining the recommended temperature and humidity levels, are essential for achieving the epoxy floor’s intended strength and durability.
High-Performance Epoxy Flooring Systems
Epoxy flooring systems can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements in specialized environments.
Chemical-resistant epoxy floors for industrial settings: Chemical-resistant epoxy formulations are designed to withstand exposure to harsh chemicals and acids, making them ideal for laboratories, manufacturing plants, and industrial facilities.
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) epoxy flooring for electronic environments: ESD epoxy flooring is engineered to dissipate electrostatic charges, providing a safe environment for sensitive electronic equipment and devices.
Self-leveling epoxy systems for seamless and level surfaces: Self-leveling epoxy is an excellent option for achieving a smooth, seamless, and level surface, ideal for areas like showrooms, retail spaces, and warehouses.
Enhancing Epoxy Flooring: Additives and Topcoats
Epoxy flooring can be customized with various additives and topcoats to enhance its performance and visual appeal.
Incorporating decorative flakes and quartz aggregates for aesthetic appeal: Decorative flakes and quartz aggregates can be added to the epoxy to create visually stunning floors with unique patterns and textures.
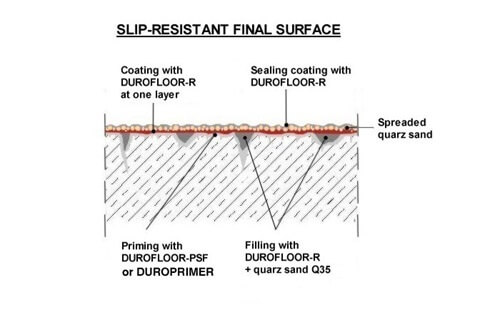
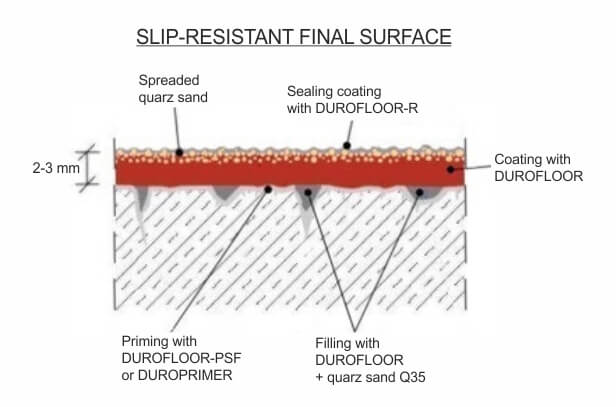
Anti-slip additives for safety in high-traffic areas: In areas prone to slips and falls, adding anti-slip aggregates to the epoxy floor provides an extra layer of safety and minimizes accidents.
The role of topcoats in enhancing durability and UV protection: Topcoats act as a protective layer, enhancing the epoxy floor’s durability and providing UV resistance to prevent yellowing or fading.
Epoxy Flooring Maintenance and Durability
Maintaining an epoxy floor properly is crucial to preserving its beauty and longevity.
Proper care and maintenance for long-lasting epoxy floors: I’ve learned that regular cleaning with mild detergents and avoiding harsh chemicals helps maintain the epoxy floor’s shine and integrity.
Factors affecting epoxy floor lifespan and performance: Heavy traffic, chemical spills, and improper maintenance can affect the epoxy floor’s lifespan and performance, making it essential to implement preventive measures.
Assessing and addressing common issues in epoxy flooring: Common issues such as delamination, bubbling, or discoloration can occur in epoxy floors. Understanding the root causes of these problems helps in effective troubleshooting and repair.
Comparing Epoxy with Other Flooring Options
Understanding the advantages of epoxy flooring compared to traditional flooring materials helps in making an informed decision.
Advantages of epoxy flooring over traditional flooring materials: Epoxy floors offer superior durability, easy maintenance, and a wide range of design options, making them a cost-effective and versatile choice.
Cost considerations and return on investment: While epoxy flooring may have a higher upfront cost than some traditional options, its long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements make it a cost-effective investment in the long run.
Epoxy vs. other resinous flooring systems (polyurethane, acrylic, etc.): Comparing epoxy with other resinous flooring systems helps in choosing the best option based on specific needs and performance requirements.
Epoxy Flooring in Green Buildings and Sustainability
The sustainability aspect of epoxy flooring makes it an attractive choice for environmentally conscious projects.
Eco-friendly aspects of epoxy flooring systems: Water-based epoxy systems with low VOC emissions contribute to improved indoor air quality and a healthier environment.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) credits for epoxy floors: Epoxy flooring systems may contribute to earning LEED credits in green building projects due to their sustainable properties.
Disposal and recycling considerations for epoxy materials: Proper disposal and recycling practices for epoxy materials contribute to minimizing environmental impact.
Safety and Health Considerations
Ensuring safety during epoxy flooring installation is crucial for both installers and occupants.
Understanding VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) in epoxy flooring: Choosing low-VOC or VOC-free epoxy options helps reduce exposure to harmful emissions during and after installation.
Proper ventilation and protective equipment during installation: Adequate ventilation and wearing appropriate safety gear protect installers from inhaling dust particles and fumes.
Compliance with industry safety standards and regulations: Following industry safety standards and guidelines ensures a safe and successful epoxy flooring installation.
Industrial Floorings FAQs PSC Flooring Ltd. Epoxy Flooring
Technical Detail Drawings (TDD) u2013 Wolverine Coatings Corporation
Epoxy Resin Terrazzo Resinous Flooring – TERRAZZCO
Solid Color Epoxy Flooring
The Ultimate Introduction to Epoxy Flooring Flowcrete
PaliKrete Colorflake Decorative Epoxy Flooring System Palma Inc.
Construction of industrial flooring using epoxy coating – ISOMAT
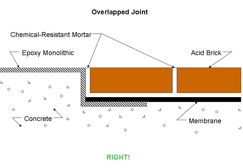
ErgonArmor – White Paper – Acid Brick-to-Epoxy Flooring Transition
Related Posts:
- Professional Epoxy Garage Floor Cost
- Wattyl Garage Floor Epoxy
- Epoxy Patio Floor
- Epoxy Garage Floor Designs
- How To Epoxy Floor Paint
- How To Apply Flakes To Epoxy Floor
- Metallic Epoxy Floor Coating Kit
- Epoxy Floor Coating Self Leveling
- Pearl Metallic Epoxy Floor Coatings
- Drawbacks Of Epoxy Flooring